Ibuprofen:
 White to off-white, crystalline powder, having a slight, characteristic odor. Practically insoluble in water; very soluble in alcohol, in methanol, in acetone, and in chloroform; slightly soluble in ethyl acetate.
White to off-white, crystalline powder, having a slight, characteristic odor. Practically insoluble in water; very soluble in alcohol, in methanol, in acetone, and in chloroform; slightly soluble in ethyl acetate.
Ichthammol:
 Reddish-brown to brownish-black, viscous fluid, having a strong, characteristic, empyreumatic odor. Miscible with water, with glycerin, and with fixed oils and fats. Partially soluble in alcohol and in ether.
Reddish-brown to brownish-black, viscous fluid, having a strong, characteristic, empyreumatic odor. Miscible with water, with glycerin, and with fixed oils and fats. Partially soluble in alcohol and in ether.
Idarubicin Hydrochloride:
 Red-orange to red-brown powder. Soluble in methanol; slightly soluble in water; insoluble in acetone and in ethyl ether.
Red-orange to red-brown powder. Soluble in methanol; slightly soluble in water; insoluble in acetone and in ethyl ether.
Idoxuridine:
 White, crystalline, practically odorless powder. Slightly soluble in water and in alcohol; practically insoluble in chloroform and in ether.
White, crystalline, practically odorless powder. Slightly soluble in water and in alcohol; practically insoluble in chloroform and in ether.
Ifosfamide:
 White, crystalline powder. Melts at about 40
White, crystalline powder. Melts at about 40 . Freely soluble in water; very soluble in alcohol, in ethyl acetate, in isopropyl alcohol, in methanol, and in methylene chloride; very slightly soluble in hexanes.
. Freely soluble in water; very soluble in alcohol, in ethyl acetate, in isopropyl alcohol, in methanol, and in methylene chloride; very slightly soluble in hexanes.
Imidurea:
 White, odorless, tasteless powder. Soluble in water and in glycerin; sparingly soluble in propylene glycol; insoluble in most organic solvents.
White, odorless, tasteless powder. Soluble in water and in glycerin; sparingly soluble in propylene glycol; insoluble in most organic solvents.
Imipenem:
 White to tan-colored crystalline powder. Sparingly soluble in water; slightly soluble in methanol.
White to tan-colored crystalline powder. Sparingly soluble in water; slightly soluble in methanol.
Imipramine Hydrochloride:
 White to off-white, odorless or practically odorless, crystalline powder. Freely soluble in water and in alcohol; soluble in acetone; insoluble in ether and in benzene.
White to off-white, odorless or practically odorless, crystalline powder. Freely soluble in water and in alcohol; soluble in acetone; insoluble in ether and in benzene.
Inamrinone:
 Pale yellow to tan powder. It is odorless or has a faint odor. Slightly soluble in methanol; practically insoluble or insoluble in chloroform and in water.
Pale yellow to tan powder. It is odorless or has a faint odor. Slightly soluble in methanol; practically insoluble or insoluble in chloroform and in water.
Indapamide:
 White to off-white, crystalline powder. Melts between 167
White to off-white, crystalline powder. Melts between 167 and 170
and 170 . Soluble in methanol, in alcohol, in acetonitrile, in glacial acetic acid, and in ethyl acetate; very slightly soluble in ether and in chloroform; practically insoluble in water.
. Soluble in methanol, in alcohol, in acetonitrile, in glacial acetic acid, and in ethyl acetate; very slightly soluble in ether and in chloroform; practically insoluble in water.
Indigotindisulfonate Sodium:
 Dusky, purplish-blue powder, or blue granules having a coppery luster. Is affected by light. Its solutions have a blue or bluish purple color. Slightly soluble in water and in alcohol; practically insoluble in most other organic solvents.
Dusky, purplish-blue powder, or blue granules having a coppery luster. Is affected by light. Its solutions have a blue or bluish purple color. Slightly soluble in water and in alcohol; practically insoluble in most other organic solvents.
Indocyanine Green:
 Olive-brown, dark green, blue-green, dark blue, or black powder. Is odorless or has a slight odor. Its solutions are deep emerald-green in color. The pH of a solution (1 in 200) is about 6. Its aqueous solutions are stable for about 8 hours. Soluble in water and in methanol; practically insoluble in most other organic solvents.
Olive-brown, dark green, blue-green, dark blue, or black powder. Is odorless or has a slight odor. Its solutions are deep emerald-green in color. The pH of a solution (1 in 200) is about 6. Its aqueous solutions are stable for about 8 hours. Soluble in water and in methanol; practically insoluble in most other organic solvents.
Indomethacin:
 Pale yellow to yellow-tan, crystalline powder, having not more than a slight odor. Is sensitive to light. Melts at about 162
Pale yellow to yellow-tan, crystalline powder, having not more than a slight odor. Is sensitive to light. Melts at about 162 . Exhibits polymorphism. Practically insoluble in water; sparingly soluble in alcohol, in chloroform, and in ether.
. Exhibits polymorphism. Practically insoluble in water; sparingly soluble in alcohol, in chloroform, and in ether.
Influenza Virus Vaccine:
 Slightly turbid liquid or suspension, which may have a slight yellow or reddish tinge and may have an odor because of the preservative.
Slightly turbid liquid or suspension, which may have a slight yellow or reddish tinge and may have an odor because of the preservative.
Inositol:
White or almost white, crystalline powder. Very soluble in water; practically insoluble in alcohol absolute and in ether.
Insulin:
 White or practically white crystals. Soluble in solutions of dilute acids and alkalies.
White or practically white crystals. Soluble in solutions of dilute acids and alkalies.
Insulin Injection:
 The Injection containing, in each mL, not more than 100 USP Units is a clear, colorless or almost colorless liquid; the Injection containing, in each mL, 500 Units may be straw-colored. Contains between 0.1% and 0.25% (w/v) of either phenol or cresol. Contains between 1.4% and 1.8% (w/v) of glycerin.
The Injection containing, in each mL, not more than 100 USP Units is a clear, colorless or almost colorless liquid; the Injection containing, in each mL, 500 Units may be straw-colored. Contains between 0.1% and 0.25% (w/v) of either phenol or cresol. Contains between 1.4% and 1.8% (w/v) of glycerin.
Insulin Lispro:
 White or practically white crystals. Soluble in solutions of dilute acids and alkalies.
White or practically white crystals. Soluble in solutions of dilute acids and alkalies.
Insulin Zinc Suspension:
 Practically colorless suspension of a mixture of characteristic crystals predominantly between 10 and 40 µm in maximum dimension and many particles that have no uniform shape and do not exceed 2 µm in maximum dimension. Contains between 0.15% and 0.17% (w/v) of sodium acetate, between 0.65% and 0.75% (w/v) of sodium chloride, and between 0.09% and 0.11% (w/v) of methylparaben.
Practically colorless suspension of a mixture of characteristic crystals predominantly between 10 and 40 µm in maximum dimension and many particles that have no uniform shape and do not exceed 2 µm in maximum dimension. Contains between 0.15% and 0.17% (w/v) of sodium acetate, between 0.65% and 0.75% (w/v) of sodium chloride, and between 0.09% and 0.11% (w/v) of methylparaben.
Isophane Insulin Suspension:
 White suspension of rod-shaped crystals, free from large aggregates of crystals following moderate agitation. Contains either (1) between 1.4% and 1.8% (w/v) of glycerin, between 0.15% and 0.17% (w/v) of metacresol, and between 0.06% and 0.07% (w/v) of phenol, or (2) between 1.4% and 1.8% (w/v) of glycerin and between 0.20% and 0.25% (w/v) of phenol. Contains between 0.15% and 0.25% (w/v) of dibasic sodium phosphate. When examined microscopically, the insoluble matter in the Suspension is crystalline, and contains not more than traces of amorphous material.
White suspension of rod-shaped crystals, free from large aggregates of crystals following moderate agitation. Contains either (1) between 1.4% and 1.8% (w/v) of glycerin, between 0.15% and 0.17% (w/v) of metacresol, and between 0.06% and 0.07% (w/v) of phenol, or (2) between 1.4% and 1.8% (w/v) of glycerin and between 0.20% and 0.25% (w/v) of phenol. Contains between 0.15% and 0.25% (w/v) of dibasic sodium phosphate. When examined microscopically, the insoluble matter in the Suspension is crystalline, and contains not more than traces of amorphous material.
Extended Insulin Zinc Suspension:
 Practically colorless suspension of a mixture of characteristic crystals the maximum dimension of which is predominantly between 10 and 40 µm. Contains between 0.15% and 0.17% (w/v) of sodium acetate, between 0.65% and 0.75% (w/v) of sodium chloride, and between 0.09% and 0.11% (w/v) of methylparaben.
Practically colorless suspension of a mixture of characteristic crystals the maximum dimension of which is predominantly between 10 and 40 µm. Contains between 0.15% and 0.17% (w/v) of sodium acetate, between 0.65% and 0.75% (w/v) of sodium chloride, and between 0.09% and 0.11% (w/v) of methylparaben.
Prompt Insulin Zinc Suspension:
 Practically colorless suspension of particles that have no uniform shape and the maximum dimension of which does not exceed 2 µm. Contains between 0.15% and 0.17% (w/v) of sodium acetate, between 0.65% and 0.75% (w/v) of sodium chloride, and between 0.09% and 0.11% (w/v) of methylparaben.
Practically colorless suspension of particles that have no uniform shape and the maximum dimension of which does not exceed 2 µm. Contains between 0.15% and 0.17% (w/v) of sodium acetate, between 0.65% and 0.75% (w/v) of sodium chloride, and between 0.09% and 0.11% (w/v) of methylparaben.
Inulin:
 White, friable, chalk-like, amorphous, odorless, tasteless powder. Soluble in hot water; slightly soluble in cold water and in organic solvents.
White, friable, chalk-like, amorphous, odorless, tasteless powder. Soluble in hot water; slightly soluble in cold water and in organic solvents.
Iodine:
 Heavy, grayish-black plates or granules, having a metallic luster and a characteristic odor. Very slightly soluble in water; freely soluble in carbon disulfide, in chloroform, in carbon tetrachloride, and in ether; soluble in alcohol and in solutions of iodides; sparingly soluble in glycerin.
Heavy, grayish-black plates or granules, having a metallic luster and a characteristic odor. Very slightly soluble in water; freely soluble in carbon disulfide, in chloroform, in carbon tetrachloride, and in ether; soluble in alcohol and in solutions of iodides; sparingly soluble in glycerin.
Iodine Topical Solution:
 Transparent, reddish-brown liquid, having the odor of iodine.
Transparent, reddish-brown liquid, having the odor of iodine.
Strong Iodine Solution:
 Transparent liquid having a deep brown color and having the odor of iodine.
Transparent liquid having a deep brown color and having the odor of iodine.
Iodine Tincture:
 Transparent liquid having a reddish-brown color and the odor of iodine and of alcohol.
Transparent liquid having a reddish-brown color and the odor of iodine and of alcohol.
Sodium Iodide I 123 Capsules:
 Capsules may contain a small amount of solid or solids, or may appear empty.
Capsules may contain a small amount of solid or solids, or may appear empty.
Sodium Iodide I 123 Solution:
 Clear, colorless solution. Upon standing, both the Solution and the glass container may darken as a result of the effects of the radiation.
Clear, colorless solution. Upon standing, both the Solution and the glass container may darken as a result of the effects of the radiation.
Iodinated I 125 Albumin Injection:
 Clear, colorless to slightly yellow solution. Upon standing, both the Albumin and the glass container may darken as a result of the effects of the radiation.
Clear, colorless to slightly yellow solution. Upon standing, both the Albumin and the glass container may darken as a result of the effects of the radiation.
Iodinated I 131 Albumin Injection:
 Clear, colorless to slightly yellow solution. Upon standing, both the Albumin and the glass container may darken as a result of the effects of the radiation.
Clear, colorless to slightly yellow solution. Upon standing, both the Albumin and the glass container may darken as a result of the effects of the radiation.
Iodinated I 131 Albumin Aggregated Injection:
 Dilute suspension of white to faintly yellow particles, which may settle on standing. The glass container may darken on standing, as a result of the effects of the radiation.
Dilute suspension of white to faintly yellow particles, which may settle on standing. The glass container may darken on standing, as a result of the effects of the radiation.
Sodium Rose Bengal I 131 Injection:
 Clear, deep-red solution.
Clear, deep-red solution.
Iodohippurate Sodium I 131 Injection:
 Clear, colorless solution. Upon standing, both the Injection and the glass container may darken as a result of the effects of the radiation.
Clear, colorless solution. Upon standing, both the Injection and the glass container may darken as a result of the effects of the radiation.
Sodium Iodide I 131 Capsules:
 May contain a small amount of solid or solids, or may appear empty.
May contain a small amount of solid or solids, or may appear empty.
Sodium Iodide I 131 Solution:
 Clear, colorless solution. Upon standing, both the Solution and the glass container may darken as a result of the effects of the radiation.
Clear, colorless solution. Upon standing, both the Solution and the glass container may darken as a result of the effects of the radiation.
Iodipamide:
 White, practically odorless, crystalline powder. Very slightly soluble in water, in chloroform, and in ether; slightly soluble in alcohol.
White, practically odorless, crystalline powder. Very slightly soluble in water, in chloroform, and in ether; slightly soluble in alcohol.
Iodipamide Meglumine Injection:
 Clear, colorless to pale yellow, slightly viscous liquid.
Clear, colorless to pale yellow, slightly viscous liquid.
Iodixanol:
 White to off-white, amorphous, odorless, hygroscopic powder. Freely soluble in water.
White to off-white, amorphous, odorless, hygroscopic powder. Freely soluble in water.
Iodoform:
 Lustrous greenish yellow powder, or lustrous crystals. It is slightly volatile even at ordinary temperatures, and distills slowly with steam. Freely soluble in ether and in chloroform; soluble in boiling alcohol; sparingly soluble in alcohol, in glycerin, and in olive oil; practically insoluble in water. Melts to a brown liquid at about 115
Lustrous greenish yellow powder, or lustrous crystals. It is slightly volatile even at ordinary temperatures, and distills slowly with steam. Freely soluble in ether and in chloroform; soluble in boiling alcohol; sparingly soluble in alcohol, in glycerin, and in olive oil; practically insoluble in water. Melts to a brown liquid at about 115 , and decomposes at a higher temperature, emitting vapors of iodine.
, and decomposes at a higher temperature, emitting vapors of iodine.
Iodoquinol:
 Light yellowish to tan, microcrystalline powder not readily wetted by water. Is odorless or has a faint odor; is stable in air. Melts with decomposition. Practically insoluble in water; sparingly soluble in alcohol and in ether.
Light yellowish to tan, microcrystalline powder not readily wetted by water. Is odorless or has a faint odor; is stable in air. Melts with decomposition. Practically insoluble in water; sparingly soluble in alcohol and in ether.
Iohexol:
 White to off-white, hygroscopic, odorless powder. Very soluble in water and in methanol; practically insoluble or insoluble in ether and in chloroform.
White to off-white, hygroscopic, odorless powder. Very soluble in water and in methanol; practically insoluble or insoluble in ether and in chloroform.
Iohexol Injection:
 Clear, colorless to pale yellow liquid.
Clear, colorless to pale yellow liquid.
Iopamidol:
 Practically odorless, white to off-white powder. Very soluble in water; sparingly soluble in methanol; practically insoluble in alcohol and in chloroform.
Practically odorless, white to off-white powder. Very soluble in water; sparingly soluble in methanol; practically insoluble in alcohol and in chloroform.
Iopanoic Acid:
 Cream-colored powder. Is tasteless or practically so, and has a faint, characteristic odor. Is affected by light. Insoluble in water; soluble in alcohol, in chloroform, and in ether; soluble in solutions of alkali hydroxides and carbonates.
Cream-colored powder. Is tasteless or practically so, and has a faint, characteristic odor. Is affected by light. Insoluble in water; soluble in alcohol, in chloroform, and in ether; soluble in solutions of alkali hydroxides and carbonates.
Iophendylate:
 Colorless to pale yellow, viscous liquid, the color darkening on long exposure to air. Is odorless or has a faintly ethereal odor. Very slightly soluble in water; freely soluble in alcohol, in benzene, in chloroform, and in ether.
Colorless to pale yellow, viscous liquid, the color darkening on long exposure to air. Is odorless or has a faintly ethereal odor. Very slightly soluble in water; freely soluble in alcohol, in benzene, in chloroform, and in ether.
Iophendylate Injection:
 Colorless to pale yellow, viscous liquid, the color darkening on long exposure to air. Is odorless or has a faintly ethereal odor. Very slightly soluble in water; freely soluble in alcohol, in benzene, in chloroform, and in ether.
Colorless to pale yellow, viscous liquid, the color darkening on long exposure to air. Is odorless or has a faintly ethereal odor. Very slightly soluble in water; freely soluble in alcohol, in benzene, in chloroform, and in ether.
Iopromide:
 White to slightly yellow powder. Freely soluble in water and in dimethyl sulfoxide; practically insoluble in alcohol, in acetone, and in ether.
White to slightly yellow powder. Freely soluble in water and in dimethyl sulfoxide; practically insoluble in alcohol, in acetone, and in ether.
Iothalamate Meglumine Injection:
 Clear, colorless to pale yellow, slightly viscous liquid.
Clear, colorless to pale yellow, slightly viscous liquid.
Iothalamate Meglumine and Iothalamate Sodium Injection:
 Clear, colorless to pale yellow, slightly viscous liquid.
Clear, colorless to pale yellow, slightly viscous liquid.
Iothalamate Sodium Injection:
 Clear, colorless to pale yellow, slightly viscous liquid.
Clear, colorless to pale yellow, slightly viscous liquid.
Iothalamic Acid:
 White, odorless powder. Slightly soluble in water and in alcohol; soluble in solutions of alkali hydroxides.
White, odorless powder. Slightly soluble in water and in alcohol; soluble in solutions of alkali hydroxides.
Ioxilan:
 White to off-white, practically odorless powder. Soluble in water and in methanol.
White to off-white, practically odorless powder. Soluble in water and in methanol.
Ioxilan Injection:
 Clear, colorless to pale yellow liquid.
Clear, colorless to pale yellow liquid.
Powdered Ipecac:
 Pale brown, weak yellow, or light olive-gray powder.
Pale brown, weak yellow, or light olive-gray powder.
Ipodate Sodium:
 White to off-white, odorless, fine, crystalline powder. Freely soluble in water, in alcohol, and in methanol; very slightly soluble in chloroform.
White to off-white, odorless, fine, crystalline powder. Freely soluble in water, in alcohol, and in methanol; very slightly soluble in chloroform.
Ipratropium Bromide:
 White to off-white, crystalline powder. Soluble in water; freely soluble in methanol; slightly soluble in alcohol.
White to off-white, crystalline powder. Soluble in water; freely soluble in methanol; slightly soluble in alcohol.
Irbesartan:
White to off-white, crystalline powder. Slightly soluble in alcohol and in methylene chloride; practically insoluble in water.
Iron Dextran Injection:
 Dark brown, slightly viscous liquid.
Dark brown, slightly viscous liquid.
Iron Sorbitex Injection:
 Clear liquid, having a dark brown color.
Clear liquid, having a dark brown color.
Isobutane:
 Colorless, flammable gas (boiling temperature is about
Colorless, flammable gas (boiling temperature is about 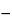 11
11 ). Vapor pressure at 21
). Vapor pressure at 21 is about 2950 mm of mercury (31 psig). NF category: Aerosol propellant.
is about 2950 mm of mercury (31 psig). NF category: Aerosol propellant.
Isoetharine Inhalation Solution:
 Colorless or slightly yellow, slightly acid liquid, gradually turning dark on exposure to air and light.
Colorless or slightly yellow, slightly acid liquid, gradually turning dark on exposure to air and light.
Isoetharine Hydrochloride:
 White to off-white, odorless, crystalline solid. Melts between 196
White to off-white, odorless, crystalline solid. Melts between 196 and 208
and 208 , with decomposition. Soluble in water; sparingly soluble in alcohol; practically insoluble in ether.
, with decomposition. Soluble in water; sparingly soluble in alcohol; practically insoluble in ether.
Isoetharine Mesylate:
 White or practically white, odorless crystals having a salty, bitter taste. Freely soluble in water; soluble in alcohol; practically insoluble in acetone and in ether.
White or practically white, odorless crystals having a salty, bitter taste. Freely soluble in water; soluble in alcohol; practically insoluble in acetone and in ether.
Isoflurane:
 Clear, colorless, volatile liquid, having a slight odor. Boils at about 49
Clear, colorless, volatile liquid, having a slight odor. Boils at about 49 . Insoluble in water. Miscible with common organic solvents and with fats and oils.
. Insoluble in water. Miscible with common organic solvents and with fats and oils.
Isoflurophate:
 Clear, colorless or faintly yellow liquid. Its vapor is extremely irritating to the eye and mucous membranes. Is decomposed by moisture, with the formation of hydrogen fluoride. Specific gravity is about 1.05. Sparingly soluble in water; soluble in alcohol and in vegetable oils.
Clear, colorless or faintly yellow liquid. Its vapor is extremely irritating to the eye and mucous membranes. Is decomposed by moisture, with the formation of hydrogen fluoride. Specific gravity is about 1.05. Sparingly soluble in water; soluble in alcohol and in vegetable oils.
Isoleucine:
 White, practically odorless crystals, having a slightly bitter taste. Soluble in water; slightly soluble in hot alcohol; insoluble in ether.
White, practically odorless crystals, having a slightly bitter taste. Soluble in water; slightly soluble in hot alcohol; insoluble in ether.
Isometheptene Mucate:
 White, crystalline powder. Freely soluble in water; soluble in alcohol; practically insoluble in chloroform and in ether.
White, crystalline powder. Freely soluble in water; soluble in alcohol; practically insoluble in chloroform and in ether.
Isoniazid:
 Colorless or white crystals or white, crystalline powder. Is odorless and is slowly affected by exposure to air and light. Freely soluble in water; sparingly soluble in alcohol; slightly soluble in chloroform; and very slightly soluble in ether.
Colorless or white crystals or white, crystalline powder. Is odorless and is slowly affected by exposure to air and light. Freely soluble in water; sparingly soluble in alcohol; slightly soluble in chloroform; and very slightly soluble in ether.
Isoniazid Injection:
 Clear, colorless to faintly greenish-yellow liquid. Gradually darkens on exposure to air and light. Tends to crystallize at low temperatures.
Clear, colorless to faintly greenish-yellow liquid. Gradually darkens on exposure to air and light. Tends to crystallize at low temperatures.
Isopropamide Iodide:
 White to pale yellow, crystalline powder, having a bitter taste. Sparingly soluble in water; freely soluble in chloroform and in alcohol; very slightly soluble in benzene and in ether.
White to pale yellow, crystalline powder, having a bitter taste. Sparingly soluble in water; freely soluble in chloroform and in alcohol; very slightly soluble in benzene and in ether.
Isopropyl Alcohol:
 Transparent, colorless, mobile, volatile liquid, having a characteristic odor and a slightly bitter taste. Is flammable. Miscible with water, with alcohol, with ether, and with chloroform. NF category: Solvent.
Transparent, colorless, mobile, volatile liquid, having a characteristic odor and a slightly bitter taste. Is flammable. Miscible with water, with alcohol, with ether, and with chloroform. NF category: Solvent.
Azeotropic Isopropyl Alcohol:
 Transparent, colorless, mobile, volatile liquid, having a characteristic odor and a slightly bitter taste. Is flammable. Miscible with water, with alcohol, with ether, and with chloroform.
Transparent, colorless, mobile, volatile liquid, having a characteristic odor and a slightly bitter taste. Is flammable. Miscible with water, with alcohol, with ether, and with chloroform.
Isopropyl Myristate:
 Clear, practically colorless, oily liquid. Is practically odorless, and congeals at about 5
Clear, practically colorless, oily liquid. Is practically odorless, and congeals at about 5 . Insoluble in water, in glycerin, and in propylene glycol; freely soluble in 90% alcohol. Miscible with most organic solvents and with fixed oils. NF category: Vehicle (oleaginous).
. Insoluble in water, in glycerin, and in propylene glycol; freely soluble in 90% alcohol. Miscible with most organic solvents and with fixed oils. NF category: Vehicle (oleaginous).
Isopropyl Palmitate:
 Colorless, mobile liquid having a very slight odor. Soluble in acetone, in castor oil, in chloroform, in cottonseed oil, in ethyl acetate, in alcohol, and in mineral oil; insoluble in water, in glycerin, and in propylene glycol. NF category: Vehicle (oleaginous).
Colorless, mobile liquid having a very slight odor. Soluble in acetone, in castor oil, in chloroform, in cottonseed oil, in ethyl acetate, in alcohol, and in mineral oil; insoluble in water, in glycerin, and in propylene glycol. NF category: Vehicle (oleaginous).
Isoproterenol Inhalation Solution:
 Colorless or practically colorless, slightly acid liquid, gradually turning dark on exposure to air and light.
Colorless or practically colorless, slightly acid liquid, gradually turning dark on exposure to air and light.
Isoproterenol Hydrochloride:
 White to practically white, odorless, crystalline powder, having a slightly bitter taste. Gradually darkens on exposure to air and light. Its solutions become pink to brownish pink on standing exposed to air, doing so almost immediately when rendered alkaline. Its solution (1 in 100) has a pH of about 5. Freely soluble in water; sparingly soluble in alcohol and less soluble in dehydrated alcohol; insoluble in chloroform and in ether.
White to practically white, odorless, crystalline powder, having a slightly bitter taste. Gradually darkens on exposure to air and light. Its solutions become pink to brownish pink on standing exposed to air, doing so almost immediately when rendered alkaline. Its solution (1 in 100) has a pH of about 5. Freely soluble in water; sparingly soluble in alcohol and less soluble in dehydrated alcohol; insoluble in chloroform and in ether.
Isoproterenol Hydrochloride Injection:
 Colorless or practically colorless liquid, gradually turning dark on exposure to air and light.
Colorless or practically colorless liquid, gradually turning dark on exposure to air and light.
Isoproterenol Sulfate:
 White to practically white, odorless, crystalline powder. It gradually darkens on exposure to air and light. Its solutions become pink to brownish pink on standing exposed to air, doing so almost immediately when rendered alkaline. A solution (1 in 100) has a pH of about 5. Freely soluble in water; very slightly soluble in alcohol, in benzene, and in ether.
White to practically white, odorless, crystalline powder. It gradually darkens on exposure to air and light. Its solutions become pink to brownish pink on standing exposed to air, doing so almost immediately when rendered alkaline. A solution (1 in 100) has a pH of about 5. Freely soluble in water; very slightly soluble in alcohol, in benzene, and in ether.
Isosorbide Concentrate:
 Colorless to slightly yellow liquid. Soluble in water and in alcohol.
Colorless to slightly yellow liquid. Soluble in water and in alcohol.
Diluted Isosorbide Dinitrate:
 Ivory-white, odorless powder. [note—Undiluted isosorbide dinitrate occurs as white, crystalline rosettes.] Undiluted isosorbide dinitrate is very slightly soluble in water; very soluble in acetone; freely soluble in chloroform; sparingly soluble in alcohol.
Ivory-white, odorless powder. [note—Undiluted isosorbide dinitrate occurs as white, crystalline rosettes.] Undiluted isosorbide dinitrate is very slightly soluble in water; very soluble in acetone; freely soluble in chloroform; sparingly soluble in alcohol.
Isotretinoin:
 Yellow crystals. Practically insoluble in water; soluble in chloroform; sparingly soluble in alcohol, in isopropyl alcohol, and in polyethylene glycol 400.
Yellow crystals. Practically insoluble in water; soluble in chloroform; sparingly soluble in alcohol, in isopropyl alcohol, and in polyethylene glycol 400.
Isoxsuprine Hydrochloride:
 White, odorless, crystalline powder, having a bitter taste. Melts at about 200
White, odorless, crystalline powder, having a bitter taste. Melts at about 200 , with decomposition. Slightly soluble in water; sparingly soluble in alcohol.
, with decomposition. Slightly soluble in water; sparingly soluble in alcohol.
Isradipine:
 Yellow, fine crystalline powder.
Yellow, fine crystalline powder.
Ivermectin:
White to yellowish-white, crystalline powder. Slightly hygroscopic. Freely soluble in methanol and in methylene chloride; soluble in acetone and in acetonitrile; practically insoluble in hexane and in water.