- British Pharmacopoeia Volume I & II
- Monographs: Medicinal and Pharmaceutical Substances
Buflomedil Hydrochloride |
 |
(Ph. Eur. monograph 1398)
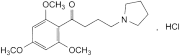
C17H25NO4,HCl 343.9 35543-24-9
Vasodilator.
Ph Eur
4-(Pyrrolidin-1-yl)-1-(2,4,6-trimethoxyphenyl)butan-1-one hydrochloride.
98.5 per cent to 101.5 per cent (dried substance).
White or almost white, microcrystalline powder.
Freely soluble in water, soluble in ethanol (96 per cent), very slightly soluble in acetone.
About 195 °C, with decomposition.
First identification B, D.
Second identification A, C, D.
A. Ultraviolet and visible absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.25).
Test solution Dissolve 25.0 mg in ethanol (96 per cent) R and dilute to 50.0 mL with the same solvent. Dilute 2.0 mL of the solution to 20.0 mL with ethanol (96 per cent) R.
Spectral range 220-350 nm.
Absorption maximum At 275 nm.
Specific absorbance at the absorption maximum 143 to 149.
B. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison buflomedil hydrochloride CRS.
C. Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).
Test solution Dissolve 40 mg of the substance to be examined in methanol R and dilute to 2 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution Dissolve 40 mg of buflomedil hydrochloride CRS in methanol R and dilute to 2 mL with the same solvent.
Plate TLC silica gel F254 plate R.
Mobile phase triethylamine R, 2-propanol R, toluene R (5:50:50 V/V/V).
Application 10 µL.
Development Over 3/4 of the plate.
Drying In air.
Detection Examine in ultraviolet light at 254 nm.
Results The principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution is similar in position and size to the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution.
D. It gives reaction (a) of chlorides (2.3.1).
Dissolve 2.5 g in carbon dioxide-free water R and dilute to 50 mL with the same solvent.
Solution S is clear (2.2.1) and colourless (2.2.2, Method II).
5.0 to 6.5 for solution S.
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Test solution Dissolve 0.10 g of the substance to be examined in the mobile phase and dilute to 10.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (a) Dilute 0.5 mL of the test solution to 100.0 mL with the mobile phase. Dilute 5.0 mL of this solution to 10.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (b) Dissolve 2 mg of buflomedil impurity B CRS in the mobile phase, add 0.5 mL of the test solution and dilute to 100.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (c) Dissolve the contents of a vial of buflomedil for peak identification CRS (containing impurities A and C) in 1.0 mL of reference solution (b).
- — size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
- — stationary phase: end-capped octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 µm);
- — temperature: 40 °C.
Mobile phase Mix 45 volumes of acetonitrile R1 and 55 volumes of a 9.25 g/L solution of potassium dihydrogen phosphate R adjusted to pH 2.5 with phosphoric acid R.
Flow rate 1 mL/min.
Detection Spectrophotometer at 210 nm.
Injection 10 µL of the test solution and reference solutions (a) and (c).
Run time Twice the retention time of buflomedil.
Identification of impurities Use the chromatogram supplied with buflomedil for peak identification CRS and the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c) to identify the peaks due to impurities A, B and C.
Relative retention With reference to buflomedil (retention time = about 5 min): impurity B = about 0.6; impurity C = about 0.7; impurity A = about 1.5.
System suitability Reference solution (c):
- — resolution: minimum 1.5 between the peaks due to impurity B and impurity C.
- — impurities A, B, C: for each impurity, not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.25 per cent);
- — unspecified impurities: for each impurity, not more than 0.4 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.10 per cent);
- — total: not more than twice the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.5 per cent);
- — disregard limit: 0.2 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.05 per cent).
Maximum 10 ppm.
2.0 g complies with test C. Prepare the reference solution using 2 mL of lead standard solution (10 ppm Pb) R.
Maximum 0.5 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by drying in an oven at 105 °C for 2 h.
Maximum 0.1 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
Dissolve 0.300 g in 15 mL of anhydrous acetic acid R and add 35 mL of acetic anhydride R. Titrate with 0.1 M perchloric acid, determining the end-point potentiometrically (2.2.20).
1 mL of 0.1 M perchloric acid is equivalent to 34.39 mg of C17H26ClNO4.
Specified impurities: A, B, C.
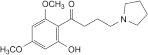
A. 1-(2-hydroxy-4,6-dimethoxyphenyl)-4-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)butan-1-one,
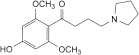
B. 1-(4-hydroxy-2,6-dimethoxyphenyl)-4-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)butan-1-one,
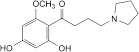
C. 1-(2,4-dihydroxy-6-methoxyphenyl)-4-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)butan-1-one.
Ph Eur

