- British Pharmacopoeia Volume I & II
- Monographs: Medicinal and Pharmaceutical Substances
Enalapril Maleate |
 |
(Ph. Eur. monograph 1420)
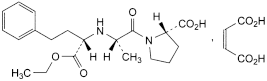
C20H28N2O5,C4H4O4 492.5 76095-16-4
Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor.
Ph Eur
(2S)-1-[(2S)-2-[[(1S)-1-(Ethoxycarbonyl)-3-phenylpropyl]amino]propanoyl]pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid (Z)-butenedioate.
98.5 per cent to 101.5 per cent (dried substance).
White or almost white, crystalline powder.
Sparingly soluble in water, freely soluble in methanol, practically insoluble in methylene chloride. It dissolves in dilute solutions of alkali hydroxides.
About 144 °C.
Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison enalapril maleate CRS.
Dissolve 0.25 g in carbon dioxide-free water R and dilute to 25.0 mL with the same solvent.
Solution S is clear (2.2.1) and colourless (2.2.2, Method II).
2.4 to 2.9 for solution S.
- 48 to - 51 (dried substance), determined on solution S.
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Buffer solution A Dissolve 2.8 g of sodium dihydrogen phosphate monohydrate R in 950 mL of water R. Adjust to pH 2.5 with phosphoric acid R and dilute to 1000 mL with water R.
Buffer solution B Dissolve 2.8 g of sodium dihydrogen phosphate monohydrate R in 950 mL of water R. Adjust to pH 6.8 with strong sodium hydroxide solution R and dilute to 1000 mL with water R.
Dissolution mixture Mix 50 mL of acetonitrile R1 and 950 mL of buffer solution A.
Test solution Dissolve 30 mg of the substance to be examined in the dissolution mixture and dilute to 100.0 mL with the dissolution mixture.
Reference solution (a) Dilute 1.0 mL of the test solution to 100.0 mL with the dissolution mixture.
Reference solution (b) Dissolve 3 mg of enalapril for system suitability CRS (containing impurity A) in the dissolution mixture and dilute to 10.0 mL with the dissolution mixture.
Reference solution (c) Dissolve the contents of a vial of enalapril impurity mixture CRS (impurities B, C, D, E and H) in 1.0 mL of the dissolution mixture.
- — size: l = 0.15 m, Ø = 4.1 mm;
- — stationary phase: styrene-divinylbenzene copolymer R (5 µm);
- — temperature: 70 °C.
- — mobile phase A: mix 50 mL of acetonitrile R1 and 950 mL of buffer solution B;
- — mobile phase B: mix 340 mL of buffer solution B and 660 mL of acetonitrile R1;

Flow rate 1.0 mL/min.
Detection Spectrophotometer at 215 nm.
Injection 50 µL.
- — use the chromatogram supplied with enalapril impurity mixture CRS and the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c) to identify the peaks due to impurities B, C, D, E and H;
- — use the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) to identify the peak due to impurity A.
Relative retention With reference to enalapril (retention time = about 11 min): impurity C = about 0.2; impurity B = about 0.8; impurity A = about 1.1; impurity H = about 1.3; impurity E = about 1.5; impurity D = about 2.1.
System suitability Reference solution (b):
- — peak-to-valley ratio: minimum 10, where Hp = height above the baseline of the peak due to impurity A and Hv = height above the baseline of the lowest point of the curve separating this peak from the peak due to enalapril.
- — impurity A: not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (1.0 per cent);
- — impurities B, C, D, E, H: for each impurity, not more than 0.3 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.3 per cent);
- — unspecified impurities: for each impurity, not more than 0.1 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.10 per cent);
- — sum of impurities other than A: not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (1.0 per cent);
- — disregard limit: 0.05 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.05 per cent); disregard the peak due to maleic acid.
Maximum 10 ppm.
2.0 g complies with test C. Prepare the reference solution using 2 mL of lead standard solution (10 ppm Pb) R.
Maximum 1.0 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by drying in an oven at 105 °C for 3 h.
Maximum 0.1 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
Dissolve 0.100 g in carbon dioxide-free water R and dilute to 30 mL with the same solvent. Titrate with 0.1 M sodium hydroxide determining the end-point potentiometrically (2.2.20). Titrate to the 2nd point of inflexion.
1 mL of 0.1 M sodium hydroxide is equivalent to 16.42 mg of C24H32N2O9.
Protected from light.
Specified impurities A, B, C, D, E, H.
Other detectable impurities (the following substances would, if present at a sufficient level, be detected by one or other of the tests in the monograph. They are limited by the general acceptance criterion for other/unspecified impurities and/or by the general monograph Substances for pharmaceutical use (2034). It is therefore not necessary to identify these impurities for demonstration of compliance. See also 5.10. Control of impurities in substances for pharmaceutical use): F, G, I.
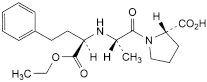
A. (2S)-1-[(2S)-2-[[(1R)-1-(ethoxycarbonyl)-3-phenylpropyl]amino]propanoyl]pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid,
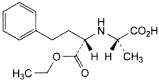
B. (2S)-2-[[(1S)-1-(ethoxycarbonyl)-3-phenylpropyl]amino]propanoic acid,
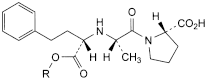
C. R = H: (2S)-1-[(2S)-2-[[(1S)-1-carboxy-3-phenylpropyl]amino]propanoyl]pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid,
E. R = CH2-CH2-C6H5: (2S)-1-[(2S)-2-[[(1S)-3-phenyl-1-[(2phenylethoxy)carbonyl]propyl]amino]propanoyl]pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid,
F. R = C4H9: (2S)-1-[(2S)-2-[[(1S)-1-(butoxycarbonyl)-3-phenylpropyl]amino]propanoyl]pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid,
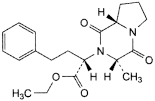
D. ethyl (2S)-2-[(3S,8aS)-3-methyl-1,4-dioxo-octahydropyrrolo[1,2-a]pyrazin-2-yl]-4-phenylbutanoate,
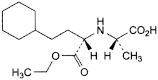
G. (2S)-2-[[(1S)-3-cyclohexyl-1-(ethoxycarbonyl)propyl]amino]propanoic acid,
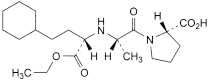
H. (2S)-1-[(2S)-2-[[(1S)-3-cyclohexyl-1-(ethoxycarbonyl)propyl]amino]propanoyl]pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid,
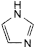
I. 1H-imidazole.
Ph Eur

