- British Pharmacopoeia Volume I & II
- Monographs: Medicinal and Pharmaceutical Substances
Ferrous Fumarate |
 |
(Ph. Eur. monograph 0902)
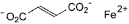
C4H2FeO4 169.9 141-01-5
Used in prevention and treatment of anaemias.
Ferrous Fumarate Oral Suspension
Ferrous Fumarate and Folic Acid Tablets
Ferrous Fumarate contains in 200 mg about 65 mg of iron.
Ph Eur
Iron(II) (E)-butenedioate.
93.0 per cent to 101.0 per cent (dried substance).
Fine, reddish-orange or reddish-brown powder.
Slightly soluble in water, very slightly soluble in ethanol (96 per cent).
A. Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).
Test solution To 1.0 g add 25 mL of a mixture of equal volumes of hydrochloric acid R and water R and heat on a water-bath for 15 min. Cool and filter. Use the filtrate for identification test C. Wash the residue with 50 mL of a mixture of 1 volume of dilute hydrochloric acid R and 9 volumes of water R and discard the washings. Dry the residue at 100-105 °C. Dissolve 20 mg of the residue in acetone R and dilute to 10 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution Dissolve 20 mg of fumaric acid CRS in acetone R and dilute to 10 mL with the same solvent.
Plate TLC silica gel F254 plate R.
Mobile phase anhydrous formic acid R, methylene chloride R, butanol R, heptane R (12:16:32:44 V/V/V/V).
Application 5 µL.
Development In an unsaturated tank, over a path of 10 cm.
Drying At 105 °C for 15 min.
Detection Examine in ultraviolet light at 254 nm.
Results The principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution is similar in position and size to the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution.
B. Mix 0.5 g with 1 g of resorcinol R. To 0.5 g of the mixture in a crucible add 0.15 mL of sulfuric acid R and heat gently. A dark red semi-solid mass is formed. Add the mass, with care, to 100 mL of water R. An orange-yellow colour develops and the solution shows no fluorescence.
C. The filtrate obtained during preparation of the test solution in identification test A gives reaction (a) of iron (2.3.1).
Dissolve 2.0 g in a mixture of 10 mL of lead-free hydrochloric acid R and 80 mL of water R, heating slightly if necessary. Allow to cool, filter if necessary and dilute to 100 mL with water R.
Maximum 0.2 per cent.
Heat 0.15 g with 8 mL of dilute hydrochloric acid R and 20 mL of distilled water R. Cool in iced water, filter and dilute to 30 mL with distilled water R.
Maximum 5 ppm.
Mix 1.0 g with 15 mL of water R and 15 mL of sulfuric acid R. Warm to precipitate the fumaric acid completely. Cool and add 30 mL of water R. Filter. Wash the precipitate with water R. Dilute the combined filtrate and washings to 125 mL with water R. 25 mL of the solution complies with the test.
Maximum 2.0 per cent.
In a flask with a ground-glass stopper, dissolve 3.0 g in a mixture of 10 mL of hydrochloric acid R and 100 mL of water R by heating rapidly to boiling. Boil for 15 s. Cool rapidly, add 3 g of potassium iodide R, stopper the flask and allow to stand protected from light for 15 min. Add 2 mL of starch solution R as indicator. Titrate the liberated iodine with 0.1 M sodium thiosulfate. Carry out a blank test. The difference between the volumes used in the 2 titrations corresponds to the amount of iodine liberated by ferric ion.
1 mL of 0.1 M sodium thiosulfate is equivalent to 5.585 mg of ferric ion.
Maximum 10 ppm
Atomic absorption spectrometry (2.2.23, Method I).
Test solution Solution S.
Reference solutions Prepare the reference solutions using cadmium standard solution (0.1 per cent Cd) R and diluting with a 10 per cent V/V solution of lead-free hydrochloric acid R.
Source Cadmium hollow-cathode lamp.
Wavelength 228.8 nm.
Atomisation device Air-acetylene flame.
Maximum 200 ppm.
Atomic absorption spectrometry (2.2.23, Method I).
Test solution Solution S.
Reference solutions Prepare the reference solutions using chromium standard solution (0.1 per cent Cr) R and diluting with a 10 per cent V/V solution of lead-free hydrochloric acid R.
Source Chromium hollow-cathode lamp.
Wavelength 357.9 nm.
Atomisation device Air-acetylene flame.
Maximum 20 ppm.
Atomic absorption spectrometry (2.2.23, Method I).
Test solution Solution S.
Reference solutions Prepare the reference solutions using lead standard solution (10 ppm Pb) R and diluting with a 10 per cent V/V solution of lead-free hydrochloric acid R.
Source Lead hollow-cathode lamp.
Wavelength 283.3 nm.
Atomisation device Air-acetylene flame.
Maximum 1 ppm.
Atomic absorption spectrometry (2.2.23, Method I).
Test solution Solution S.
Reference solutions Prepare the reference solutions using mercury standard solution (10 ppm Hg) R and diluting with a 25 per cent V/V solution of lead-free hydrochloric acid R.
Source Mercury hollow-cathode lamp.
Wavelength 253.7 nm.
Following the recommendations of the manufacturer, introduce 5 mL of solution S or 5 mL of the reference solutions into the reaction vessel of the cold-vapour mercury assay accessory, add 10 mL of water R and 1 mL of stannous chloride solution R1.
Maximum 200 ppm.
Atomic absorption spectrometry (2.2.23, Method I).
Test solution Solution S.
Reference solutions Prepare the reference solutions using nickel standard solution (10 ppm Ni) R and diluting with a 10 per cent V/V solution of lead-free hydrochloric acid R.
Source Nickel hollow-cathode lamp.
Wavelength 232 nm.
Atomisation device Air-acetylene flame.
Maximum 500 ppm.
Atomic absorption spectrometry (2.2.23, Method I).
Test solution Solution S diluted to 10 volumes.
Reference solutions Prepare the reference solutions using zinc standard solution (10 ppm Zn) R and diluting with a 1 per cent V/V solution of lead-free hydrochloric acid R.
Source Zinc hollow-cathode lamp.
Wavelength 213.9 nm.
Atomisation device Air-acetylene flame.
Maximum 1.0 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by drying in an oven at 105 °C.
Dissolve with slight heating 0.150 g in 7.5 mL of dilute sulfuric acid R. Cool and add 25 mL of water R. Add 0.1 mL of ferroin R. Titrate immediately with 0.1 M cerium sulfate until the colour changes from orange to light bluish-green.
1 mL of 0.1 M cerium sulfate is equivalent to 16.99 mg of C4H2FeO4.
In an airtight container, protected from light.
Ph Eur

