- British Pharmacopoeia Volume I & II
- Monographs: Medicinal and Pharmaceutical Substances
Glycerol Monostearate 40-55 |
 |
(Ph. Eur. monograph 0495)
31566-31-1
Excipient.
Ph Eur
Mixture of monoacylglycerols, mainly monostearoylglycerol, together with variable quantities of di- and triacylglycerols. It is obtained by partial glycerolysis of vegetable oils mainly containing triacylglycerols of palmitic (hexadecanoic) or stearic (octadecanoic) acid or by esterification of glycerol with stearic acid. The fatty acids may be of vegetable or animal origin.
- — monoacylglycerols: 40.0 per cent to 55.0 per cent;
- — diacylglycerols: 30.0 per cent to 45.0 per cent;
- — triacylglycerols: 5.0 per cent to 15.0 per cent.
Hard, waxy mass or unctuous powder or flakes, white or almost white.
Practically insoluble in water, soluble in ethanol (96 per cent) at 60 °C.
First identification C, D.
Second identification A, B.
A. Melting point (2.2.15): 54 °C to 66 °C.
Introduce the melted substance into the capillary tubes and allow to stand for 24 h in a well-closed container.
B. Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).
Test solution Dissolve 0.5 g of the substance to be examined in methylene chloride R, with gentle heating, and dilute to 10 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution Dissolve 0.5 g of glycerol monostearate 40-55 CRS in methylene chloride R, with gentle heating, and dilute to 10 mL with the same solvent.
Plate TLC silica gel plate R.
Mobile phase hexane R, ether R (30:70 V/V).
Application 10 µL.
Development Over a path of 15 cm.
Detection Spray with a 0.1 g/L solution of rhodamine B R in ethanol (96 per cent) R and examine in ultraviolet light at 365 nm.
Suitability system Reference solution:
- — the chromatogram shows 4 clearly separated spots.
Results The spots in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution are similar in position to those in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution.
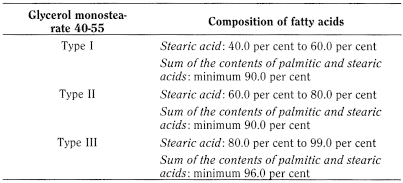
C. Composition of fatty acids (see Tests) according to the type stated on the label.
D. It complies with the limits of the assay (monoacylglycerol content).
Maximum 3.0, determined on 1.0 g.
Use a mixture of equal volumes of ethanol (96 per cent) R and toluene R as solvent and heat gently.
Maximum 3.0.
158 to 177, determined on 2.0 g. Carry out the titration with heating.
Maximum 6.0 per cent, determined as described under Assay.
Use the mixture of calibrating substances in Table 2.4.22.-1.
Composition of the fatty-acid fraction of the substance:
Maximum 1 ppm.
Maximum 1.0 per cent, determined on 1.00 g. Use pyridine R as the solvent and heat gently.
Maximum 0.1 per cent.
Size-exclusion chromatography (2.2.30).
Test solution Into a 15 mL flask, weigh 0.200 g (m). Add 5.0 mL of tetrahydrofuran R and shake to dissolve. Reweigh the flask and calculate the total mass of solvent and substance (M).
Reference solutions Into four 15 mL flasks, respectively weigh 2.5 mg, 5.0 mg, 10.0 mg and 20.0 mg of glycerol R, and add 5.0 mL of tetrahydrofuran R to each flask. Weigh the flasks again and calculate the concentration of glycerol in milligrams per gram for each reference solution.
- — size: l = 0.6 m, Ø = 7 mm;
- — stationary phase: styrene-divinylbenzene copolymer R (5 µm) with a pore size of 10 nm.
Mobile phase tetrahydrofuran R.
Flow rate 1 mL/min.
Detection Differential refractometer.
Injection 40 µL.
Relative retention With reference to glycerol (retention time = about 15 min): triacylglycerols = about 0.75; diacylglycerols = about 0.80; monoacylglycerols = about 0.85.
- — free glycerol : from the calibration curve obtained with the reference solutions, determine the concentration (C) in milligrams per gram in the test solution and calculate the percentage content in the substance to be examined using the following expression:
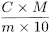
- — mono-, di- and triacylglycerols: calculate the percentage contents by the normalisation procedure.
The label states the type of glycerol monostearate 40-55.
Ph Eur

