- British Pharmacopoeia Volume I & II
- Monographs: Medicinal and Pharmaceutical Substances
Paracetamol |
 |
(Ph. Eur. monograph 0049)
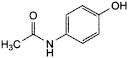
C8H9NO2 151.2 103-90-2
Analgesic; antipyretic.
Effervescent Co-codamol Tablets
Paediatric Paracetamol Oral Solution
Paediatric Paracetamol Oral Suspension
Paracetamol and Caffeine Tablets
Soluble Paracetamol and Caffeine Tablets
Dispersible Paracetamol Tablets
Paracetamol, Codeine Phosphate and Caffeine Capsules
Paracetamol, Codeine Phosphate and Caffeine Tablets
Ph Eur
N-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)acetamide.
99.0 per cent to 101.0 per cent (dried substance).
White or almost white, crystalline powder.
Sparingly soluble in water, freely soluble in alcohol, very slightly soluble in methylene chloride.
First identification A, C.
Second identification A, B, D, E.
A. Melting point (2.2.14): 168 °C to 172 °C.
B. Dissolve 0.1 g in methanol R and dilute to 100.0 mL with the same solvent. To 1.0 mL of the solution add 0.5 mL of a 10.3 g/L solution of hydrochloric acid R and dilute to 100.0 mL with methanol R. Protect the solution from bright light and immediately measure the absorbance (2.2.25) at the absorption maximum at 249 nm. The specific absorbance at the maximum is 860 to 980.
C. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Preparation Discs.
Comparison paracetamol CRS.
D. To 0.1 g add 1 mL of hydrochloric acid R, heat to boiling for 3 min, add 1 mL of water R and cool in an ice bath. No precipitate is formed. Add 0.05 mL of a 4.9 g/L solution of potassium dichromate R. A violet colour develops which does not change to red.
E. It gives the reaction of acetyl (2.3.1). Heat over a naked flame.
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29). Prepare the solutions immediately before use.
Test solution Dissolve 0.200 g of the substance to be examined in 2.5 mL of methanol R containing 4.6 g/L of a 400 g/L solution of tetrabutylammonium hydroxide R and dilute to 10.0 mL with a mixture of equal volumes of a 17.9 g/L solution of disodium hydrogen phosphate R and of a 7.8 g/L solution of sodium dihydrogen phosphate R.
Reference solution (a) Dilute 1.0 mL of the test solution to 50.0 mL with the mobile phase. Dilute 5.0 mL of this solution to 100.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (b) Dilute 1.0 mL of reference solution (a) to 10.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (c) Dissolve 5.0 mg of 4-aminophenol R, 5 mg of paracetamol CRS and 5.0 mg of chloroacetanilide R in methanol R and dilute to 20.0 mL with the same solvent. Dilute 1.0 mL to 250.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (d) Dissolve 20.0 mg of 4-nitrophenol R in methanol R and dilute to 50.0 mL with the same solvent. Dilute 1.0 mL to 20.0 mL with the mobile phase.
- — size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4.6 mm,
- — stationary phase: octylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 µm),
- — temperature: 35 °C.
Mobile phase Mix 375 volumes of a 17.9 g/L solution of disodium hydrogen phosphate R, 375 volumes of a 7.8 g/L solution of sodium dihydrogen phosphate R and 250 volumes of methanol R containing 4.6 g/L of a 400 g/L solution of tetrabutylammonium hydroxide R.
Flow rate 1.5 mL/min.
Detection Spectrophotometer at 245 nm.
Injection 20 µL.
Run time 12 times the retention time of paracetamol.
Relative retentions With reference to paracetamol (retention time = about 4 min): impurity K = about 0.8; impurity F = about 3; impurity J = about 7.
System suitability Reference solution (c):
- — resolution: minimum 4.0 between the peaks due to impurity K and to paracetamol,
- — signal-to-noise ratio: minimum 50 for the peak due to impurity J.
- — impurity J: not more than 0.2 times the area of the corresponding peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c) (10 ppm),
- — impurity K: not more than the area of the corresponding peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c) (50 ppm),
- — impurity F: not more than half the area of the corresponding peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (d) (0.05 per cent),
- — any other impurity: not more than half the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.05 per cent),
- — total of other impurities: not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.1 per cent),
- — disregard limit for the calculation of the total of other impurities: the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.01 per cent).
Maximum 20 ppm.
Dissolve 1.0 g in a mixture of 15 volumes of water R and 85 volumes of acetone R and dilute to 20 mL with the same mixture of solvents. 12 mL of the solution complies with limit test B. Prepare the standard using lead standard solution (1 ppm Pb) obtained by diluting lead standard solution (100 ppm Pb) R with a mixture of 15 volumes of water R and 85 volumes of acetone R.
Maximum 0.5 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by drying in an oven at 105 °C.
Maximum 0.1 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
Dissolve 0.300 g in a mixture of 10 mL of water R and 30 mL of dilute sulfuric acid R. Boil under a reflux condenser for 1 h, cool and dilute to 100.0 mL with water R. To 20.0 mL of the solution add 40 mL of water R, 40 g of ice, 15 mL of dilute hydrochloric acid R and 0.1 mL of ferroin R. Titrate with 0.1 M cerium sulfate until a greenish-yellow colour is obtained. Carry out a blank titration.
1 mL of 0.1 M cerium sulfate is equivalent to 7.56 mg of C8H9NO2.
Protected from light.
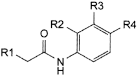
A. R1 = R3 = R4 = H, R2 = OH: N-(2-hydroxyphenyl)acetamide,
B. R1 = CH3, R2 = R3 = H, R4 = OH: N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanamide,
C. R1 = R2 = H, R3 = Cl, R4 = OH: N-(3-chloro-4-hydroxyphenyl)acetamide,
D. R1 = R2 = R3 = R4 = H: N-phenylacetamide,
H. R1 = R2 = R3 = H, R4 = O-CO-CH3: 4-(acetylamino)phenyl acetate,
J. R1 = R2 = R3 = H, R4 = Cl: N-(4-chlorophenyl)acetamide (chloroacetanilide),
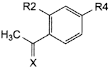
E. X = O, R2 = H, R4 = OH: 1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)ethanone,
G. X = N-OH, R2 = H, R4 = OH: 1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)ethanone oxime,
I. X = O, R2 = OH, R4 = H: 1-(2-hydroxyphenyl)ethanone,
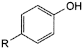
F. R = NO2: 4-nitrophenol,
K. R = NH2: 4-aminophenol.
Ph Eur

