- British Pharmacopoeia Volume I & II
- Monographs: Medicinal and Pharmaceutical Substances
Rutoside Trihydrate |
 |
(Ph. Eur. monograph 1795)
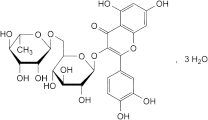
C27H30O16,3H2O 665 250249-75-3
Bioflavinoid.
Ph Eur
3-[[6-O-(6-Deoxy-α-l-mannopyranosyl)-β-d-glucopyranosyl]oxy]-2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5,7-dihydroxy-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one.
95.0 per cent to 101.0 per cent (anhydrous substance).
Yellow or greenish-yellow, crystalline powder.
Practically insoluble in water, soluble in methanol, sparingly soluble in ethanol (96 per cent), practically insoluble in methylene chloride. It dissolves in solutions of alkali hydroxides.
First identification B.
Second identification A, C, D.
A. Ultraviolet and visible absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.25).
Test solution Dissolve 50.0 mg in methanol R, dilute to 250.0 mL with the same solvent and filter if necessary. Dilute 5.0 mL of the solution to 50.0 mL with methanol R.
Spectral range 210-450 nm.
Absorption maxima At 257 nm and 358 nm.
Specific absorbance at the absorption maximum at 358 nm 305 to 330 (anhydrous substance).
B. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison rutoside trihydrate CRS.
C. Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).
Test solution Dissolve 25 mg of the substance to be examined in methanol R and dilute to 10.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution Dissolve 25 mg of rutoside trihydrate CRS in methanol R and dilute to 10.0 mL with the same solvent.
Plate TLC silica gel G plate R.
Mobile phase butanol R, anhydrous acetic acid R, water R, methyl ethyl ketone R, ethyl acetate R (5:10:10:30:50 V/V/V/V/V).
Application 10 µL.
Development Over a path of 10 cm.
Drying In air.
Detection Spray with a mixture of 2.5 mL of ferric chloride solution R1 and 7.5 mL of a 10 g/L solution of potassium ferricyanide R and examine for 10 min.
Results The principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution is similar in position, colour and size to the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution.
D. Dissolve 10 mg in 5 mL of ethanol (96 per cent) R, add 1 g of zinc R and 2 mL of hydrochloric acid R1. A red colour develops.
The absorbance (2.2.25) is not greater than 0.10 at wavelengths between 450 nm and 800 nm.
Dissolve 0.200 g in 40 mL of 2-propanol R. Stir for 15 min, dilute to 50.0 mL with 2-propanol R and filter.
Maximum 3 per cent.
Shake 2.5 g of the substance to be examined for 15 min in 50 mL of methanol R at 20-25 °C. Filter under reduced pressure through a sintered-glass filter (1.6) (2.1.2) previously dried for 15 min at 100-105 °C, allowed to cool in a desiccator and tared. Wash the filter 3 times with 20 mL of methanol R. Dry the filter for 30 min at 100-105 °C. Allow to cool and weigh. The residue weighs a maximum of 75 mg.
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Test solution Dissolve 0.10 g of the substance to be examined in 20 mL of methanol R and dilute to 100.0 mL with mobile phase B.
Reference solution (a) Dissolve 10.0 mg of rutoside trihydrate CRS in 2.0 mL of methanol R and dilute to 10.0 mL with mobile phase B.
Reference solution (b) Dilute 1.0 mL of reference solution (a) to 50.0 mL with mobile phase B.
- — size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4.0 mm;
- — stationary phase: octylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 µm);
- — temperature: 30 °C.
- — mobile phase A: mix 5 volumes of tetrahydrofuran R and 95 volumes of a 15.6 g/L solution of sodium dihydrogen phosphate R adjusted to pH 3.0 with phosphoric acid R;
- — mobile phase B: mix 40 volumes of tetrahydrofuran R and 60 volumes of a 15.6 g/L solution of sodium dihydrogen phosphate R adjusted to pH 3.0 with phosphoric acid R;
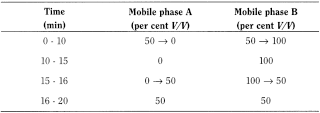
Flow rate 1 mL/min.
Detection Spectrophotometer at 280 nm.
Injection 20 µL.
Relative retention With reference to rutoside (retention time = about 7 min): impurity B = about 1.1; impurity A = about 1.2; impurity C = about 2.5.
System suitability Reference solution (a):
- — resolution: minimum 2.5 between the peaks due to rutoside and impurity B.
Limits Locate the impurities by comparison with the chromatogram provided with rutoside trihydrate CRS:
- — correction factors: for the calculation of content, multiply the peak areas of the following impurities by the corresponding correction factor: impurity A = 0.8; impurity C = 0.5;
- — impurities A, B, C: for each impurity, not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (2.0 per cent);
- — total: not more than twice the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (4.0 per cent);
- — disregard limit: 0.05 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.1 per cent).
7.5 per cent to 9.5 per cent, determined on 0.100 g.
Maximum 0.1 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
Dissolve 0.200 g in 20 mL of dimethylformamide R. Titrate with 0.1 M tetrabutylammonium hydroxide, determining the end-point potentiometrically (2.2.20).
1 mL of 0.1 M tetrabutylammonium hydroxide is equivalent to 30.53 mg of C27H30O16.
Protected from light.
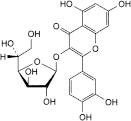
A. 2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-3-(β-d-glucofuranosyloxy)-5,7-dihydroxy-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one (isoquercitroside),
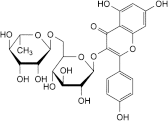
B. 3-[[6-O-(6-deoxy-α-l-mannopyranosyl)-β-d-glucopyranosyl]oxy]-5,7-dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one (kaempferol 3-rutinoside),
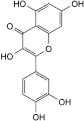
C. 2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-3,5,7-trihydroxy-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one (quercetin).
Ph Eur

