- British Pharmacopoeia Volume III
- Formulated Preparations: Specific Monographs
Bupivacaine Heavy Injection |
Bupivacaine and Dextrose Injection; Bupivacaine and Glucose Injection
Local anaesthetic.
Bupivacaine Heavy Injection is a sterile solution of Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and either Anhydrous Glucose or Glucose in Water for Injections. No preservative is added. The inclusion of glucose in the formulation assists the gravitational flow of the injection when administered.
The injection complies with the requirements stated under Parenteral Preparations and with the following requirements.
95.0 to 105.0% of the stated amount.
72.0 to 88.0 mg per mL.
A clear, colourless solution.
A. To a volume of the injection containing 50 mg of Bupivacaine Hydrochloride add sufficient 2m sodium hydroxide to obtain a pH of 11 and extract with 25 mL of n-heptane. Dry the heptane extract over anhydrous sodium sulfate, filter, evaporate the filtrate to dryness using a rotary evaporator and dry at 60° at a pressure of 2 kPa for 16 hours. The infrared absorption spectrum of the dried residue, Appendix II A, is concordant with the reference spectrum of bupivacaine (RS 034).
B. Dip, for 1 second, a suitable stick with a reactive pad containing glucose-oxidase, peroxidase and a hydrogen-donating substance, such as tetramethylbenzidine, in the injection. Observe the colour of the reactive pad; within 60 seconds the colour changes from yellow to green or blue.
C. In the Assay for bupivacaine, the chromatogram obtained with solution (1) shows a peak with the same retention time as the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2).
D. When heated with cupri-tartaric solution R1, a copious precipitate of copper(i) oxide is produced.
pH, 4.0 to 6.0, Appendix V L.
To 27.6g of sodium dihydrogen phosphate monohydrate add 7 mL of a solution containing 8.9% of disodium hydrogen orthophosphate dihydrate and add sufficient water to produce 1000 mL, if necessary adjust the pH to 5.0 using 1m orthophosphoric acid or 1m sodium hydroxide (buffer solution).
Carry out the method for liquid chromatography, Appendix III D, using the following solutions in the mobile phase.
(1) Dilute a volume of the injection with mobile phase if necessary to contain 0.5% w/v of Bupivacaine Hydrochloride.
(2) 0.0004% w/v of 2,6-dimethylaniline.
(3) 0.0002% w/v of 2,6-dimethylaniline and 0.0002% w/v 4-chloroaniline.
(a) Use a stainless steel column (25 cm × 4.6 mm) packed with end-capped octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography (5 µm) (Hypersil Elite is suitable).
(b) Use isocratic elution and the mobile phase described below.
(c) Use a flow rate of 1.0 mL per minute.
(d) Use ambient column temperature.
(e) Use an electrochemical detector (direct amperometry) with a glassy carbon working electrode, a silver-silver chloride reference electrode, held at + 0.9 V oxidation potential, and a detector sensitivity of 20 nA/V.
(f) Inject volume of 20 µL of each solution.
Under the prescribed conditions the retention time of 2,6-dimethylaniline is about 6.5 minutes.
A mixture of 4 volumes of acetonitrile and 6 volumes of buffer solution containing 0.006% w/v disodium edetate and 0.055% w/v tetrabutylammonium hydrogen sulfate R1.
The test is not valid unless, in the chromatogram obtained with solution (3), the resolution factor between the peaks corresponding to 2,6-dimethylaniline and 4-chloroaniline is at least 1.5.
In the chromatogram obtained with solution (1):
the area of any peak corresponding to 2,6-dimethylaniline is not greater than the area of any corresponding peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (800 ppm).
Dilute a volume of the injection containing 1.0 g of Glucose Monohydrate to 250 mL with water. The absorbance of the resulting solution at the maximum at 284 nm is not more than 0.25, Appendix II B.
To 0.18g of sodium dihydrogen phosphate monohydrate and 2.9g of disodium hydrogen orthophosphate dihydrate add sufficient water to produce 1000 mL, if necessary adjust the pH to 8.0 using 1m orthophosphoric acid or 1m sodium hydroxide (buffer solution).
Carry out the method for liquid chromatography, Appendix III D, using the following solutions.
(1) Dilute a volume of the injection if necessary to contain 0.5% w/v of Bupivacaine Hydrochloride.
(2) Dilute 1 volume of solution (1) to 200 volumes.
(3) Dilute 1 volume of solution (2) to 10 volumes.
(a) Use a stainless steel column (15 cm × 3.9 mm) packed with octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography (10 µm) (µBondapak is suitable).
(b) Use isocratic elution and the mobile phase described below.
(c) Flow rate of 1.5 mL per minute.
(d) Use ambient column temperature.
(e) Use a detection wavelength 240nm.
(f) Inject 20 µL of each solution.
A mixture of 4 volumes of buffer solution and 6 volumes of acetonitrile.
In the chromatogram obtained with solution (1):
the area of any secondary peak is not greater than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (0.5%);
the total area of any secondary peaks is not greater than twice the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (1.0%);
Disregard any peak with an area less than that of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (3) (0.05%) and any peak corresponding to 2,6-dimethylaniline.
Carry out the method for liquid chromatography, Appendix III D, using the following solutions in the mobile phase.
(1) Dilute a volume of the injection if necessary to contain 0.05% w/v of Bupivacaine Hydrochloride.
(2) 0.05% w/v of bupivacaine hydrochloride BPCRS.
The chromatographic conditions described under Related substances may be used.
Calculate the content of C18H28N2O,HCl,H2O in the injection using the declared content of C18H28N2O,HCl,H2O in bupivacaine hydrochloride BPCRS.
To a quantity containing the equivalent of 2 to 5 g of glucose, C6H12O6, add 0.2 mL of 5M ammonia and sufficient water to produce 100 mL. Mix well, allow to stand for 30 minutes and measure the optical rotation in a 2-dm tube, Appendix V F. The observed rotation in degrees multiplied by 0.9477 represents the weight in g of glucose, C6H12O6, in the quantity of the injection taken for assay.
The strength is stated in terms of the equivalent amount of bupivacaine hydrochloride and in terms of the equivalent amount of glucose, C6H12O6 in a suitable dose-volume.
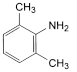
A. 2,6-Dimethylaniline,
B. 5-hydroxymethylfurfural.

