- British Pharmacopoeia Volume III
- Formulated Preparations: Specific Monographs
Oxybutynin Tablets |
Anticholinergic.
Oxybutynin Tablets contain Oxybutynin Hydrochloride.
The tablets comply with the requirements stated under Tablets and with the following requirements.
95.0 to 105.0% of the stated amount.
To a quantity of the powdered tablets containing 25 mg of Oxybutynin Hydrochloride add sufficient 2m sodium hydroxide to adjust to pH 12.0 and extract with four 20-mL quantities of hexane. Filter the collected hexane layers through anhydrous sodium sulfate (Whatman GF/C is suitable). Evaporate the filtrate to dryness under a current of nitrogen, to yield a clear, sticky liquid residue. The infrared absorption spectrum of the residue, Appendix II A, is concordant with the reference spectrum of oxybutynin (RS442).
Comply with the requirements for Monographs of the British Pharmacopoeia in the dissolution test for tablets and capsules, Appendix XII B1.
(a) Use Apparatus 2, rotating the paddle at 50 revolutions per minute.
(b) Use 900 mL of water, at a temperature of 37°, as the medium.
Carry out the method for liquid chromatography, Appendix III D, using the following solutions.
(1) After 45 minutes withdraw a sample of 20 mL of the medium, filter through a 0.45-µm membrane filter and discard the first 10 mL of filtrate. Use the filtered dissolution medium diluted, if necessary, to produce a solution containing 0.0005% w/v of Oxybutynin Hydrochloride
(2) 0.0005% w/v of oxybutynin hydrochloride BPCRS.
The chromatographic conditions described under Assay may be used.
Calculate the total content of Oxybutynin Hydrochloride, C22H31NO3,HCl, in the medium from the chromatograms obtained and using the declared content of C22H31NO3,HCl in oxybutynin hydrochloride BPCRS.
Carry out the method for liquid chromatography, Appendix III D, using the following solutions.
(1) Mix a quantity of the powdered tablets containing 50 mg of Oxybutynin Hydrochloride with 40 mL of 0.01m hydrochloric acid with the aid of ultrasound for 15 minutes, add sufficient 0.01m hydrochloric acid to produce 50 mL, mix and filter (Whatman GF/A filters are suitable).
(2) 0.0015% w/v of oxybutynin impurity A EPCRS in 0.01m hydrochloric acid.
(3) 0.001% w/v of phenylcyclohexylglycolic acid BPCRS in 0.01m hydrochloric acid.
(4) Dilute 1 volume of solution (1) to 200 volumes with 0.01m hydrochloric acid.
(5) 0.001% w/v of oxybutynin impurity A EPCRS in solution (4).
(a) Use a stainless steel column (15 cm × 4.6 mm) packed with octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R1 (5 µm) (Symmetry C18 is suitable).
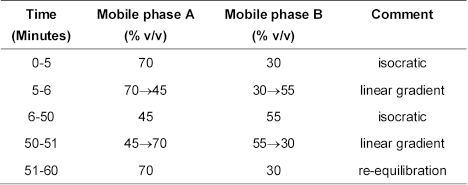
(b) Use gradient elution and the mobile phases described below.
(c) Use a flow rate of 1 mL per minute.
(d) Use an ambient column temperature.
(e) Use a detection wavelength of 210 nm.
(f) Inject 50 µL of each solution.
(g) When the chromatograms are recorded under the prescribed conditions the retention times are about 31 minutes for oxybutynin hydrochloride and about 47 minutes for oxybutynin impurity A.
Mobile phase A 0.34% w/v of potassium dihydrogen orthophosphate and 0.436% w/v of dipotassium hydrogen orthophosphate.
Mobile phase B acetonitrile R1.
The test is not valid unless, in the chromatogram obtained with solution (5), the resolution factor between the peaks due to oxybutynin hydrochloride and oxybutynin impurity A is at least 10.0.
In the chromatogram obtained with solution (1);
the area of any peak corresponding to oxybutynin impurity A is not greater than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (1.5%);
the area of any peak corresponding to phenylcyclohexylglycolic acid is not greater than half the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (3) (0.5%);
the area of any other secondary peak is not greater than 0.4 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (4) (0.2%);
the sum of the areas of any such secondary peaks is not greater than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (4) (0.5%).
Disregard any peak with an area less than 0.1 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (4) (0.05%).
Carry out the method for liquid chromatography, Appendix III D, using the following solutions.
(1) Mix 10 whole tablets with 400 mL of 0.01m hydrochloric acid for 20 minutes with the aid of ultrasound, cool, add sufficient 0.01m hydrochloric acid to produce 500 mL, mix and filter (Whatman GF/A filters are suitable). Dilute a volume of this solution with sufficient 0.01m hydrochloric acid to produce a solution containing 0.005% w/v of Oxybutynin Hydrochloride.
(2) 0.005% w/v of oxybutynin hydrochloride BPCRS in 0.01m hydrochloric acid.
(a) Use a stainless steel column (15 cm × 4.6 mm) packed with nitrile silica gel for chromatography R1 (5 µm) (Spherisorb nitrile is suitable).
(b) Use isocratic elution and the mobile phase described below.
(c) Use a flow rate of 2 mL per minute.
(d) Use a column temperature 40°.
(e) Use a detection wavelength of 200 nm.
(f) Inject 20 µL of each solution.
300 volumes of acetonitrile R1 and 700 volumes of a 0.48% w/v solution of anhydrous potassium dihydrogen orthophosphate previously adjusted to pH 3.0 to 3.5 with orthophosphoric acid.
Calculate the content of C22H31NO3,HCl in the tablets using the declared content of C22H31NO3,HCl in oxybutynin hydrochloride BPCRS.
The impurities limited by the requirements of this monograph include:

1. 4-(diethylamino)but-2-ynyl (RS)-2-(cyclohex-3-enyl)-2-cyclohexyl-2-hydroxyacetate (European Pharmacopoeia impurity A),

2. (RS)-2-cyclohexyl-2-hydroxy-2-phenylacetic acid (phenylcyclohexylglycolic acid) (European Pharmacopoeia impurity D).

