- British Pharmacopoeia Volume III
- Formulated Preparations: Specific Monographs
Paediatric Vitamins A, C and D Oral Drops |
Paediatric Vitamins A, C and D Oral Drops are a solution of vitamin A, Ascorbic Acid and Colecalciferol in a suitable, flavoured vehicle.
The oral drops comply with the requirements stated under Oral Liquids and with the following requirements.
5200 to 6200 IU per mL.
160 to 175 mg per mL.
2100 to 2500 IU per mL.
A. In the Assay for vitamin A, the solution shows a maximum at 325 nm.
B. Carry out the method for thin-layer chromatography, Appendix III A, using the following solutions.
(1) Dilute the oral drops, if necessary, with water to contain the equivalent of 0.5% w/v of ascorbic acid.
(2) 0.5% w/v of ascorbic acid BPCRS in water.
(a) Use as the coating TLC silica gel F254 plate (Merck silica gel 60 F254 plates are suitable).
(b) Use the mobile phase as described below.
(c) Apply 2 µL of each solution.
(d) Develop the plate to 15 cm.
(e) After removal of the plate, dry in air and examine under ultraviolet light (254 nm).
20 volumes of water and 120 volumes of ethanol (96%).
The principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with solution (1) corresponds in position and colour to that in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2).
C. In the Assay for colecalciferol, the chromatogram obtained with solution (1) shows a peak corresponding to the colecalciferol peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2).
Carry out the test as rapidly as possible, avoiding exposure to actinic light and air, oxidising agents, oxidation catalysts (e.g. copper and iron) and acids.
Examine by ultraviolet absorption spectrophotometry, Appendix II B (Method A). If method A is found not to be valid, examine by liquid chromatography, Appendix III D (Method B).
Test solution To a weighed quantity of the oral drops containing 50,000 IU in a round-bottomed flask, add 3 mL of a freshly prepared 50% w/w solution of potassium hydroxide and 30 mL of absolute ethanol. Boil under a reflux condenser in a current of nitrogen for 30 minutes. Cool rapidly and add 30 mL of water. Extract with four 50 mL quantities of ether discarding the lower layer after complete separation. Wash the combined upper layers with four 50 mL quantities of water and evaporate to dryness under a gentle current of nitrogen at a temperature not exceeding 30° or in a rotary evaporator at a temperature not exceeding 30° under reduced pressure (water ejector). Dissolve the residue in sufficient propan-2-ol to give an expected concentration of vitamin A equivalent to 10 to 15 IU per mL.
Measure the absorbances, Appendix II B, of the solution at 300 nm, 310 nm, 325 nm and 334 nm and at the wavelength of maximum absorption with a suitable spectrophotometer in 1 cm matched cells, using propan-2-ol as the compensation liquid.
Calculate the content of vitamin A, as all-trans-retinol, in IU per gram from the expression:
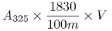
where |
A 325 |
= |
absorbance at 325 nm |
m |
= |
weight of the oral drops in grams |
|
V |
= |
total volume of solution containing 10 IU to 15 IU of vitamin A per mL |
|
1830 |
= |
conversion factor for the specific absorbance of all-trans-retinol in IU |
The above expression can be used only if A325 has a value of not greater than A325, corr / 0.970 where A325, corr is the corrected absorbance at 325 nm and is given by the equation:
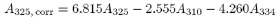
where A designates the absorbance at the wavelength indicated by the subscript.
If A325 has a value greater than A325, corr / 0.970, calculate the content of vitamin A from the expression:
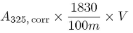
The assay is not valid unless:
(a) the wavelength of maximum absorption lies between 323 nm and 327 nm and
(b) the absorbance at 300 nm relative to that at 325 nm is at most 0.73.
Carry out the method for liquid chromatography, Appendix III D, using the following solutions.
(1) To a weighed quantity of the oral drops containing 50,000 IU in a round-bottomed flask, add 5 mL of a freshly prepared 10% w/v solution of ascorbic acid and 10 mL of a freshly prepared 80% w/v solution of potassium hydroxide and 100 mL of ethanol (96%). Boil under a reflux condenser on a water bath for 15 minutes. Add 100 mL of a 1% w/v solution of sodium chloride and cool. Transfer the solution to a 500 mL separating funnel rinsing the round-bottomed flask with about 75 mL of a 1% w/v solution of sodium chloride and then with 150 mL of a mixture of equal volumes of petroleum spirit (boiling range, 40° to 60°) and ether. Shake for 1 minute. When the layers have separated completely, discard the lower layer and wash the upper layer, first with 50 mL of a 3% w/v solution of potassium hydroxide in a 10% v/v solution of ethanol (96%) and then with three 50 mL quantities of a 1% w/v solution of sodium chloride. Filter the upper layer through 5 g of anhydrous sodium sulfate on a fast filter paper into a 250 mL flask suitable for a rotary evaporator. Wash the funnel with 10 mL of fresh extraction mixture, filter and combine the upper layers. Distil them at a temperature not exceeding 30° under reduced pressure (water ejector) and fill with nitrogen when evaporation is completed. Alternatively evaporate the solvent under a gentle current of nitrogen at a temperature not exceeding 30°. Dissolve the residue in propan-2-ol, transfer to a 25 mL volumetric flask and dilute to 25 mL with propan-2-ol. Gentle heating in an ultrasonic bath may be required.
(2) Prepare a solution of retinyl acetate EPCRS in propan-2-ol R1 so that 1 mL contains about 1000 IU of all-trans-retinol.
The exact concentration of solution (2) is assessed by ultraviolet absorption spectrophotometry, Appendix II B. Dilute solution (2) with propan-2-ol R1 to a presumed concentration of 10 to 15 IU per mL and measure the absorbance at 326 nm in matched 1 cm cells using propan-2-ol R1 as the compensation liquid.
Calculate the content of vitamin A in IU per mL of solution (2) from the following expression, taking into account the assigned content of retinyl acetate EPCRS:
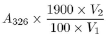
where |
A 326 |
= |
absorbance at 326 nm |
V 2 |
= |
volume of the diluted solution |
|
V 1 |
= |
volume of solution (2) used |
|
1900 |
= |
conversion factor for the specific absorbance of retinyl acetate EPCRS in IU |
For solution (3) proceed as described for solution (1) but use 2 mL of solution (2) in place of the oral drops.
The exact concentration of solution (3) is assessed by ultraviolet absorption spectrophotometry, Appendix II B. Dilute solution (3) with propan-2-ol R1 to a presumed concentration of 10 to 15 IU per mL of all-trans-retinol and measure the absorbance at 325 nm in matched 1 cm cells using propan-2-ol R1 as the compensation liquid.
Calculate the content of all-trans-retinol in IU per millilitre of solution (3) from the expression:
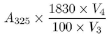
where |
A 325 |
= |
absorbance at 325 nm |
V 3 |
= |
volume of the diluted solution |
|
V 4 |
= |
volume of solution (3) used |
|
1830 |
= |
conversion factor for the specific absorbance of all-trans-retinol in IU |
(a) Use a stainless steel column (25 cm × 4.6 mm) packed with octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography (5 µm to 10 µm).
(b) Use isocratic elution and the mobile phase described below.
(c) Use a flow rate of 1 mL per minute.
(d) Use an ambient column temperature.
(e) Use a detection wavelength of 325 nm.
(f) Inject 10 µL of each solution.
3 volumes of water and 97 volumes of methanol.
Inject in triplicate solution (1) and solution (3). The retention time of all-trans-retinol is 5 ± 1 minutes.
The assay is not valid unless: (a) the chromatogram obtained with solution (1) shows a peak corresponding to that of all-trans-retinol in the chromatogram obtained with solution (3); (b) when using the method of standard additions to solution (1) there is greater than 95% recovery of the added retinyl acetate EPCRS; (c) the recovery of all-trans-retinol in solution (3), as assessed by direct absorption spectrophotometry, is greater than 95%.
Calculate the content of vitamin A using the following expression:
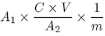
where |
A 1 |
= |
area of the peak corresponding to all-trans-retinol in the chromatogram obtained with solution (1) |
A 2 |
= |
area of the peak corresponding to all-trans-retinol in the chromatogram obtained with solution (3) |
|
C |
= |
concentration of retinyl acetate EPCRS in solution (2) as assessed prior to the saponification in International Units per mL (= 1000 IU per mL) |
|
V |
= |
volume of solution (2) treated |
|
m |
= |
weight of the oral drops in solution (1) |
To a volume of the oral drops containing the equivalent of 0.14 g of ascorbic acid, add 100 mL of 1% w/v orthophosphoric acid in water and 1 mL of starch solution and titrate with 0.05m iodine VS until a full blue colour is produced. Each mL of 0.05m iodine VS is equivalent to 0.0088 g of ascorbic acid.
Carry out the assay as rapidly as possible, avoiding exposure to actinic light and air. Carry out the method for liquid chromatography, Appendix III D, using the following solutions.
(1) To a weighed quantity of the oral drops containing about 4000 IU of colecalciferol, add 10 mL of a 0.001% w/v solution of ergocalciferol BPCRS in absolute ethanol, 20 mL of absolute ethanol and 5 mL of a 60% w/v solution of potassium hydroxide in water. Pass a stream of nitrogen and boil under a reflux condenser for 20 minutes, cool and transfer the contents to a separating funnel using ether, shake and allow the layers to separate; discard the lower layer and wash the ether layer with four 50 mL quantities of water, swirling gently for each washing and discard the lower layer. Evaporate to dryness using a rotary evaporator and transfer the residue to a 4 mL vial using small quantities of methanol until 4 mL of solution is obtained.
(2) In the same manner as solution (1) but using 10 mL each of 0.001% w/v each of colecalciferol BPCRS and ergocalciferol BPCRS respectively beginning at the words '20 mL of absolute ethanol...'.
(a) Use a stainless steel column (25 cm × 4.6 mm) packed with particles of silica the surface of which has been modified with chemically-bonded octadecylsilyl groups (5 µm) (Spherisorb ODS 1 is suitable).
(b) Use isocratic elution and the mobile phase described below. Allow the mobile phase to equilibrate for 30 minutes.
(c) Use a flow rate of 1.5 mL per minute.
(d) Use an ambient column temperature.
(e) Use a detection wavelength of 254 nm.
(f) Inject 20 µL of each solution.
7 volumes of water and 93 volumes of methanol.
The assay is not valid unless the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) shows two distinct peaks. If complete resolution is not attained, add 3% v/v of distilled water to the mobile phase, allow to equilibrate and repeat the chromatography. If the resolution is still not achieved, use a new column and allow the mobile phase to equilibrate for 30 minutes.
Determine the weight per mL of the oral drops, Appendix V G, and calculate the content of colecalciferol, weight in volume, using the declared content of colecalciferol in colecalciferol BPCRS.
Paediatric Vitamins A, C and D Oral Drops should be kept in an airtight container and protected from light.
The label states the number of International Units of Vitamin A and Colecalciferol and the content of vitamin C in terms of the equivalent amount of ascorbic acid.

