- British Pharmacopoeia Volume I & II
- Monographs: Medicinal and Pharmaceutical Substances
Stearic Acid |
 |
(Ph. Eur. monograph 1474)
Excipient.
Ph Eur
Mixture consisting mainly of stearic (octadecanoic) acid (C18H36O2; Mr 284.5) and palmitic (hexadecanoic) acid (C16H32O2; Mr 256.4) obtained from fats or oils of vegetable or animal origin.
White or almost white, waxy, flaky crystals, white or almost white hard masses, or white or yellowish-white powder.
Practically insoluble in water, soluble in ethanol (96 per cent) and in light petroleum (bp: 50-70 °C).
A. Freezing point (see Tests).
B. Acid value (2.5.1): 194 to 212, determined on 0.5 g.
C. Examine the chromatograms obtained in the assay.
Results The principal peaks in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution are similar in retention time to those in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution.
Heat the substance to be examined to about 75 °C. The resulting liquid is not more intensely coloured than reference solution Y7 or BY7 (2.2.2, Method I).
Melt 5.0 g, shake for 2 min with 10 mL of hot carbon dioxide-free water R, cool slowly and filter. To the filtrate add 0.05 mL of methyl orange solution R. No red colour develops.
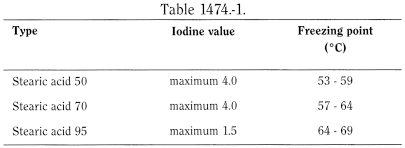
See Table 1474.-1.
See Table 1474.-1.
Maximum 1 ppm.
Gas chromatography (2.2.28): use the normalisation procedure.
Test solution In a conical flask fitted with a reflux condenser, dissolve 0.100 g of the substance to be examined in 5 mL of boron trifluoride-methanol solution R. Boil under reflux for 10 min. Add 4.0 mL of heptane R through the condenser and boil again under reflux for 10 min. Allow to cool. Add 20 mL of a saturated solution of sodium chloride R. Shake and allow the layers to separate. Remove about 2 mL of the organic layer and dry it over 0.2 g of anhydrous sodium sulfate R. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 10.0 mL with heptane R.
Reference solution Prepare the reference solution in the same manner as the test solution using 50 mg of palmitic acid CRS and 50 mg of stearic acid CRS instead of the substance to be examined.
- — material: fused silica;
- — size: l = 30 m, Ø = 0.32 mm;
- — stationary phase: macrogol 20 000 R (film thickness 0.5 µm).
Carrier gas helium for chromatography R.
Flow rate 2.4 mL/min.

Detection Flame ionisation.
Injection 1 µL.
Relative retention With reference to methyl stearate: methyl palmitate = about 0.9.
System suitability Reference solution:
- — resolution: minimum 5.0 between the peaks due to methyl palmitate and methyl stearate;
- — repeatability: maximum relative standard deviation of 3.0 per cent for the areas of the peaks due to methyl palmitate and methyl stearate, after 6 injections; maximum 1.0 per cent for the ratio of the areas of the peaks due to methyl palmitate to the areas of the peaks due to methyl stearate, after 6 injections.
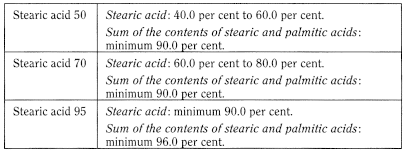
The label states the type of stearic acid (50, 70, 95).
This section provides information on characteristics that are recognised as being relevant control parameters for one or more functions of the substance when used as an excipient (see chapter 5.15). This section is a non-mandatory part of the monograph and it is not necessary to verify the characteristics to demonstrate compliance. Control of these characteristics can however contribute to the quality of a medicinal product by improving the consistency of the manufacturing process and the performance of the medicinal product during use. Where control methods are cited, they are recognised as being suitable for the purpose, but other methods can also be used. Wherever results for a particular characteristic are reported, the control method must be indicated.
The following characteristics may be relevant for stearic acid used as a lubricant in tablets and capsules.
Ph Eur