- British Pharmacopoeia Volume III
- Formulated Preparations: Specific Monographs
Insulin Zinc Suspension |
 |
Insulin Zinc Suspension, Mixed
(Insulin Zinc Injectable Suspension, Ph Eur monograph 0837)
Hormone; treatment of diabetes mellitus.
Ph Eur
Insulin zinc injectable suspension complies with the monograph on Insulin preparations, injectable (0854) with the amendments prescribed below.
Insulin zinc injectable suspension is a sterile neutral suspension of bovine insulin and/or porcine insulin or of human insulin with a suitable zinc salt; the insulin is in a form which is practically insoluble in water.
Insulin zinc injectable suspension is prepared by carrying out the procedures described in the monograph on Insulin preparations, injectable (0854).
Insulin zinc injectable suspension is produced by mixing insulin zinc injectable suspension (crystalline) and insulin zinc injectable suspension (amorphous) in a ratio of 7 to 3.
A white or almost white suspension which on standing deposits a white or almost white sediment and leaves a colourless or almost colourless supernatant liquid; the sediment is readily resuspended by gently shaking. When examined under a microscope, the majority of the particles are seen to be rhombohedral crystals with a maximum dimension when measured from corner to corner through the crystal greater than 10 µm but rarely exceeding 40 µm; a considerable proportion of the particles are seen to have no uniform shape and a maximum dimension rarely exceeding 2 µm.
Examine the chromatograms obtained in the Assay.
For preparations made from a single species of insulin (bovine, porcine or human), the position of the peak due to insulin in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution corresponds to that of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with the appropriate reference solution. For preparations made from a mixture of bovine and porcine insulin, the positions of the peaks due to the two insulins in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution correspond to those of the principal peaks in the chromatogram obtained with the appropriate reference solution.
63 per cent to 77 per cent of the total insulin content. Centrifuge a volume of the substance to be examined containing 200 IU of insulin and discard the supernatant liquid. Suspend the residue in 1.65 mL of water R, add 3.3 mL of buffered acetone solution R, stir for 3 min, again centrifuge, discard the supernatant liquid and repeat all the operations with the residue. Dissolve the residue using a suitable procedure, for example dissolve in 0.1 M hydrochloric acid to give a final volume of 2.0 mL. Determine the insulin content of the residue (R) and determine the total insulin content (T) of an equal volume of the suspension by a suitable method. Calculate the percentage of insulin not extractable with buffered acetone solution from the expression:
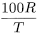
0.12 mg to 0.25 mg per 100 IU of insulin, determined as described in the monograph on Insulin preparations, injectable (0854).
20 per cent to 65 per cent of the total zinc is in the form of zinc in solution. Determine by the method described in the monograph on Insulin preparations, injectable (0854).
Ph Eur