Polonovski Reaction; Potier-Polonovski Reaction
M. Polonovski, M. Polonovski, Bull. Soc. Chim. France 41, 1190 (1927).
Rearrangement of tertiary amine oxides upon treatment with acetic anhydride or acetyl chloride, in which one of the alkyl groups attached to the nitrogen is cleaved, generating the N,N-disubstituted acetamide and aldehyde:
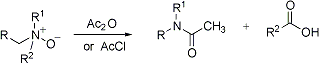
Reviews: A. R. Katritzky, J. N. Lagowski, Chemistry of Heterocyclic N-Oxides (Academic Press, New York, 1971) p 279, 362; D. Grierson, Org. React. 39, 85-295 (1990); D. S. Grierson, H.-P. Husson, Comp. Org. Syn. 6, 909-924 (1991).
The reaction proceeds via an iminium ion intermediate which becomes the stable reaction product when trifluoroacetic anhydride is employed. This modified procedure is commonly referred to as the Potier-Polonovski reaction: A. Cave et al., Tetrahedron 23, 4681 (1967); T. Tamminen et al., ibid. 45, 2683 (1989); R. J. Sundberg, et al., ibid. 48, 277 (1992).