Galageenan
» Galageenan is the hydrocolloid obtained by extraction with water or aqueous alkali from the red seaweed class Rhodophyceae species Eucheuma gelatinae. Galageenan consists chiefly of potassium, sodium, calcium, magnesium, and ammonium sulfate esters of galactose and 3,6-anhydrogalactose copolymers. These hexoses are alternately linked in 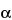 -1,3 and
-1,3 and 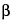 -1,4 in the polymer. The ester sulfate content ranges from 8 percent to 18 percent. In addition, it contains inorganic salts that originate from the seaweed and from the process of recovery from the extract.
-1,4 in the polymer. The ester sulfate content ranges from 8 percent to 18 percent. In addition, it contains inorganic salts that originate from the seaweed and from the process of recovery from the extract.
Galageenan is recovered by alcohol precipitation or by freezing and pressing.
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in tight containers, preferably in a cool place.
Identification—
A:
A solution (1 in 50) prepared by heating a uniform dispersion in a hot water bath to 80 (Solution A) becomes more viscous upon cooling and may form a gel.
(Solution A) becomes more viscous upon cooling and may form a gel.
B:
Dilute a portion of Solution A with about 4 parts of water, and add 2 to 3 drops of methylene blue TS: a blue, stringy precipitate is formed.
Spectral range:
2000 to 600 cm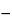 1.
1.
Test solution—
Disperse 2 g of it in 400 mL of a solution containing 5 g of edetate disodium in 1000 mL of 60% isopropyl alcohol, and stir for 2 hours. Filter with the aid of vacuum, and wash the residue with a total of 200 mL of 65% isopropyl alcohol. Finish washing with a total of 100 mL of 80% isopropyl alcohol. Dry the residue for 30 minutes in a 60 oven, and finally overnight in a 70
oven, and finally overnight in a 70 vacuum oven. Break lumps by grinding with a mortar and pestle. Dissolve 15 mg of the alcohol-treated material in 5 mL of water. Heat for 10 minutes in a water bath. Pipet 2 mL onto a suitable nonsticking surface to produce a 5-µm thick film (when dry).
vacuum oven. Break lumps by grinding with a mortar and pestle. Dissolve 15 mg of the alcohol-treated material in 5 mL of water. Heat for 10 minutes in a water bath. Pipet 2 mL onto a suitable nonsticking surface to produce a 5-µm thick film (when dry).
Procedure—
Subtract the baseline (drawn by connecting the minima in the range of 1500 and 800 cm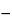 1) from the raw spectrum. Record the absorbances for the bands at 1220-1260, 928-933, 840-850, and 800-805 cm
1) from the raw spectrum. Record the absorbances for the bands at 1220-1260, 928-933, 840-850, and 800-805 cm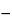 1 relative to the absorbance at 1050 cm
1 relative to the absorbance at 1050 cm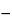 1: the absorbance values so obtained are within the ranges specified in the accompanying table.
1: the absorbance values so obtained are within the ranges specified in the accompanying table.
| Wave Number cm |
Molecular Assignment |
Absorbance Relative to 1050 cm |
| Galageenan | ||
| 1220 to 1260 | Ester sulfate | 0.3 to 0.6 |
| 928 to 933 | 3,6-anhydrogalactose | 0.3 to 0.6 |
| 840 to 850 | Galactose-4-sulfate | 0.1 to 0.3 |
| 800 to 805 | 3,6-anhydrogalactose-2-sulfate | 0.0 to 0.1 |
Viscosity  911
911 —
Transfer 7.5 g of Galageenan to a tared, tall-form, 600-mL beaker, add 450 mL of water, and disperse with agitation for about 15 minutes. Add water to bring the weight to 500 g, and heat in a water bath, with continuous agitation, until a temperature of 80
—
Transfer 7.5 g of Galageenan to a tared, tall-form, 600-mL beaker, add 450 mL of water, and disperse with agitation for about 15 minutes. Add water to bring the weight to 500 g, and heat in a water bath, with continuous agitation, until a temperature of 80 is reached. Add water to adjust for loss by evaporation, cool to between 76
is reached. Add water to adjust for loss by evaporation, cool to between 76 and 77
and 77 , and place in a constant-temperature bath maintained at 75
, and place in a constant-temperature bath maintained at 75 . Use a suitable rotational viscosimeter equipped with a spindle having a cylinder 1.88 cm in diameter and 6.51 cm in height, the immersion depth being 8.10 cm (No. 1 spindle). Allow the spindle to rotate in the solution at 30 rpm for 6 revolutions, then observe the scale reading. Convert the scale reading to centipoises by multiplying by the constant for the spindle and speed employed. The viscosity at 75
. Use a suitable rotational viscosimeter equipped with a spindle having a cylinder 1.88 cm in diameter and 6.51 cm in height, the immersion depth being 8.10 cm (No. 1 spindle). Allow the spindle to rotate in the solution at 30 rpm for 6 revolutions, then observe the scale reading. Convert the scale reading to centipoises by multiplying by the constant for the spindle and speed employed. The viscosity at 75 is not less than 15 centipoises.
is not less than 15 centipoises.
Microbial enumeration tests  61
61 and Tests for specified microorganisms
and Tests for specified microorganisms  62
62 —
The total aerobic microbial count does not exceed 200 cfu per g, the total combined molds and yeasts count does not exceed 20 cfu per g, and it meets the requirements of the tests for absence of Escherichia coli and Salmonella species.
—
The total aerobic microbial count does not exceed 200 cfu per g, the total combined molds and yeasts count does not exceed 20 cfu per g, and it meets the requirements of the tests for absence of Escherichia coli and Salmonella species.
Loss on drying  731
731 —
Dry it at a pressure not exceeding 10 mm of mercury at 70
—
Dry it at a pressure not exceeding 10 mm of mercury at 70 for 18 hours, cool in a desiccator, and weigh: it loses not more than 12.5% of its weight.
for 18 hours, cool in a desiccator, and weigh: it loses not more than 12.5% of its weight.
Acid-insoluble matter—
Transfer about 2 g of Galageenan, accurately weighed, to a 250-mL beaker containing 150 mL of water and 1.5 mL of sulfuric acid. Cover with a watch glass, and heat on a steam bath for 6 hours, rubbing down the wall of the beaker frequently with a rubber-tipped stirring rod, and replacing any water lost by evaporation. Transfer about 500 mg of a suitable filter aid, accurately weighed to the beaker, and pass through a tared filtering crucible equipped with a 2.4-cm glass fiber filter. Wash the residue several times with hot water, dry at 105 for 3 hours, cool in a desiccator, and weigh. The difference between the total weight and the sum of the weights of the filter aid, crucible, and glass fiber filter is the weight of the acid-insoluble matter. It is not more than 2.0% of the weight of Galageenan taken.
for 3 hours, cool in a desiccator, and weigh. The difference between the total weight and the sum of the weights of the filter aid, crucible, and glass fiber filter is the weight of the acid-insoluble matter. It is not more than 2.0% of the weight of Galageenan taken.
Total ash  561
561 :
not more than 35.0%.
:
not more than 35.0%.
Lead  251
251 :
0.0005%.
:
0.0005%.
Heavy metals, Method II  231
231 :
0.002%.
:
0.002%.
Content of sulfate—
Accurately weigh about 300 mg of Galageenan onto an ashless filter paper. Fold the paper so as to enclose the sample, and place it into a 500-mL Kjeldahl flask. Add 45 mL of nitric acid and bring to boil on a hot plate in a fume hood. Add nitric acid as necessary to keep the sample from evaporating to dryness. Continue boiling until digestion is complete and the volume of nitric acid remaining is about 10 mL. Cool the mixture, and reduce the excess nitric acid by adding formaldehyde TS until the evolution of nitrogen oxide vapors has ceased. Heat this mixture on a hot plate to reduce the volume to about 10 mL. Transfer the mixture to a 150-mL beaker with the aid of several portions of water until the total volume is approximately 100 mL. Add 0.5 mL of hydrochloric acid, and bring to a boil on a hot plate. Add carefully 10 mL of 0.25 M barium chloride, and allow to boil for 1 minute. Cover with a watch glass, and allow to stand overnight. Filter the solution through a tared, fine-porosity filtering crucible previously ignited in a muffle furnace at 550 for 30 minutes and cooled in a desiccator for 30 minutes. Wash the barium sulfate precipitate so obtained on the crucible several times with boiling water, place the crucible in an oven, and heat at 100
for 30 minutes and cooled in a desiccator for 30 minutes. Wash the barium sulfate precipitate so obtained on the crucible several times with boiling water, place the crucible in an oven, and heat at 100 for 30 minutes. Transfer the crucible to a muffle furnace, and ignite for 30 minutes at 550
for 30 minutes. Transfer the crucible to a muffle furnace, and ignite for 30 minutes at 550 . Remove the crucible, and cool in a desiccator for 30 minutes. Weigh, and calculate the percentage of sulfate groups by the formula:
. Remove the crucible, and cool in a desiccator for 30 minutes. Weigh, and calculate the percentage of sulfate groups by the formula:
(96.02 / 233.43)(100WB / WS)
in which 233.43 and 96.02 are the molecular weights of barium sulfate and the sulfate group, respectively; WB is the weight, in mg, of barium sulfate obtained; and WS is the weight, in mg, of Galageenan taken. The percentage of sulfate is not less than 8% and not more than 18%.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
| Monograph | Hong Wang, Ph.D.
Scientist 1-301-816-8351 |
(EM205) Excipient Monographs 2 |
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Senior Scientist 1-301-816-8339 |
(MSA05) Microbiology and Sterility Assurance | |
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Senior Scientist 1-301-816-8339 |
(MSA05) Microbiology and Sterility Assurance |
USP32–NF27 Page 1239