- British Pharmacopoeia Volume I & II
- Monographs: Medicinal and Pharmaceutical Substances
Cefotaxime Sodium |
 |
(Ph. Eur. monograph 0989)
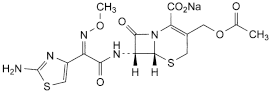
C16H16N5NaO7S2 477.4 64485-93-4
Cephalosporin antibacterial.
Ph Eur
Sodium (6R,7R)-3-[(acetyloxy)methyl]-7-[[(2Z)-2-(2-aminothiazol-4-yl)-2-(methoxyimino)acetyl]amino]-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylate.
Semi-synthetic product derived from a fermentation product.
96.0 per cent to 102.0 per cent (anhydrous substance).
White or slightly yellow powder, hygroscopic.
Freely soluble in water, sparingly soluble in methanol.
A. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison cefotaxime sodium CRS.
B. It gives reaction (a) of sodium (2.3.1).
Dissolve 2.5 g in carbon dioxide-free water R and dilute to 25.0 mL with the same solvent.
Solution S is clear (2.2.1). Add 1 mL of glacial acetic acid R to 10 mL of solution S. The solution, examined immediately, is clear.
4.5 to 6.5 for solution S.
+ 58.0 to + 64.0 (anhydrous substance).
Dissolve 0.100 g in water R and dilute to 10.0 mL with the same solvent.
Maximum 0.40 at 430 nm for solution S.
360 to 390, determined at the absorption maximum at 235 nm (anhydrous substance).
Dissolve 20.0 mg in water R and dilute to 100.0 mL with the same solvent. Dilute 10.0 mL of the solution to 100.0 mL with water R.
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29). Prepare the solutions immediately before use.
Solution A Mobile phase B, mobile phase A (14:86 V/V).
Test solution Dissolve 40.0 mg of the substance to be examined in solution A and dilute to 50.0 mL with the same solution.
Reference solution (a) Dissolve 8.0 mg of cefotaxime acid CRS in solution A and dilute to 10.0 mL with the same solution.
Reference solution (b) Dilute 1.0 mL of the test solution to 100.0 mL with solution A.
Reference solution (c) Add 1.0 mL of dilute hydrochloric acid R to 4.0 mL of the test solution. Heat the solution at 40 °C for 2 h. Add 5.0 mL of buffer solution pH 6.6 R and 1.0 mL of dilute sodium hydroxide solution R.
Reference solution (d) Dissolve 4 mg of cefotaxime for peak identification CRS (containing impurities A, B, C, E and F) in 5 mL of solution A.
- — size: l = 0.15 m, Ø = 3.9 mm,
- — stationary phase: octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 µm),
- — temperature: 30 °C.
- — mobile phase A: 7.1 g/L solution of disodium hydrogen phosphate R adjusted to pH 6.25 using phosphoric acid R;
- — mobile phase B: methanol R;
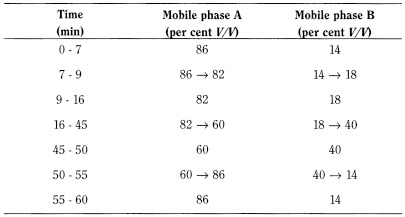
Flow rate 1.0 mL/min.
Detection Spectrophotometer at 235 nm.
Injection 10 µL of the test solution and reference solutions (b), (c) and (d).
Identification of impurities Use the chromatogram supplied with cefotaxime for peak identification CRS and the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (d) to identify the peaks due to impurities A, B, C, E and F.
Relative retention With reference to cefotaxime (retention time = about 13 min): impurity B = about 0.3; impurity A = about 0.5; impurity E = about 0.6; impurity C = about 1.9; impurity D = about 2.3; impurity F = about 2.4; impurity G = about 3.1.
System suitability Reference solution (c):
- — resolution: minimum 3.5 between the peaks due to impurity E and cefotaxime;
- — symmetry factor: maximum 2.0 for the peak due to cefotaxime.
- — impurities A, B, C, D, E, F: for each impurity, not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (1.0 per cent);
- — any other impurity: for each impurity, not more than 0.2 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.2 per cent);
- — total: not more than 3 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (3.0 per cent);
- — disregard limit: 0.05 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.05 per cent).
Maximum 1.0 per cent.
Maximum 20 ppm.
Maximum 0.5 per cent m/m.
Maximum 3.0 per cent, determined on 0.300 g.
Less than 0.05 IU/mg, if intended for use in the manufacture of parenteral preparations without a further appropriate procedure for the removal of bacterial endotoxins.
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29) as described in the test for related substances with the following modification.
Injection Test solution and reference solution (a).
Calculate the percentage content of C16H16N5NaO7S2 by multiplying the percentage content of cefotaxime by 1.048.
In an airtight container, protected from light. If the substance is sterile, store in a sterile, airtight, tamper-proof container.
Specified impurities A, B, C, D, E, F.
Other detectable impurities (the following substances would, if present at a sufficient level, be detected by one or other of the tests in the monograph. They are limited by the general acceptance criterion for other/unspecified impurities and/or by the general monograph Substances for pharmaceutical use (2034). It is therefore not necessary to identify these impurities for demonstration of compliance. See also 5.10. Control of impurities in substances for pharmaceutical use): G.
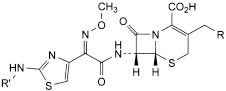
A. R = R′ = H: (6R,7R)-7-[[(2Z)-2-(2-aminothiazol-4-yl)-2-(methoxyimino)acetyl]amino]-3-methyl-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid (deacetoxycefotaxime),
B. R = OH, R′ = H: (6R,7R)-7-[[(2Z)-2-(2-aminothiazol-4-yl)-2-(methoxyimino)acetyl]amino]-3-(hydroxymethyl)-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid (deacetylcefotaxime),
C. R = O-CO-CH3, R′ = CHO: (6R,7R)-3-[(acetyloxy)methyl]-7-[[(2Z)-2-[2-(formylamino)thiazol-4-yl]-2-(methoxyimino)acetyl]amino]-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid (N-formylcefotaxime),
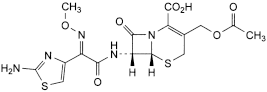
D. (6R,7R)-3-[(acetyloxy)methyl]-7-[[(2E)-2-(2-aminothiazol-4-yl)-2-(methoxyimino)acetyl]amino]-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid (E-cefotaxime),
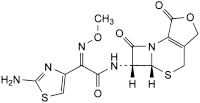
E. (5aR,6R)-6-[[(2Z)-2-(2-aminothiazol-4-yl)-2-(methoxyimino)acetyl]amino]-5a,6-dihydro-3H,7H-azeto[2,1-b]furo[3,4-d][1,3]thiazine-1,7(4H)-dione (deacetylcefotaxime lactone),
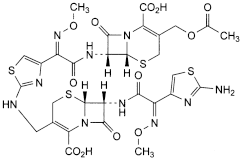
F. (6R,7R)-3-[(acetyloxy)methyl]-7-[[(2Z)-2-[2-[[[(6R,7R)-7-[[(2Z)-2-(2-aminothiazol-4-yl)-2-(methoxyimino)acetyl]amino]-2-carboxy-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-en-2-yl]methyl]amino]thiazol-4-yl]-2-(methoxyimino)acetyl]amino]-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid (cefotaxime dimer),
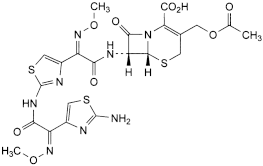
G. (6R,7R)-3-[(acetyloxy)methyl]-7-[[(2Z)-2-[2-[[(2Z)-2-(2-aminothiazol-4-yl)-2-(methoxyimino)acetyl]amino]thiazol-4-yl]-2-(methoxyimino)acetyl]amino]-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid (ATA cefotaxime).
Ph Eur

